Page 628 - Corrosion Engineering Principles and Practice
P. 628
590 C h a p t e r 1 4 P r o t e c t i v e C o a t i n g s 591
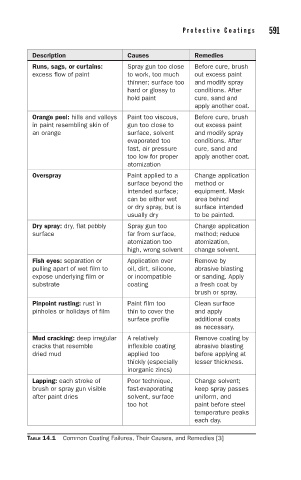
Description Causes Remedies
Runs, sags, or curtains: Spray gun too close Before cure, brush
excess flow of paint to work, too much out excess paint
thinner; surface too and modify spray
hard or glossy to conditions. After
hold paint cure, sand and
apply another coat.
Orange peel: hills and valleys Paint too viscous, Before cure, brush
in paint resembling skin of gun too close to out excess paint
an orange surface, solvent and modify spray
evaporated too conditions. After
fast, air pressure cure, sand and
too low for proper apply another coat.
atomization
Overspray Paint applied to a Change application
surface beyond the method or
intended surface; equipment. Mask
can be either wet area behind
or dry spray, but is surface intended
usually dry to be painted.
Dry spray: dry, flat pebbly Spray gun too Change application
surface far from surface, method; reduce
atomization too atomization,
high, wrong solvent change solvent.
Fish eyes: separation or Application over Remove by
pulling apart of wet film to oil, dirt, silicone, abrasive blasting
expose underlying film or or incompatible or sanding. Apply
substrate coating a fresh coat by
brush or spray.
Pinpoint rusting: rust in Paint film too Clean surface
pinholes or holidays of film thin to cover the and apply
surface profile additional coats
as necessary.
Mud cracking: deep irregular A relatively Remove coating by
cracks that resemble inflexible coating abrasive blasting
dried mud applied too before applying at
thickly (especially lesser thickness.
inorganic zincs)
Lapping: each stroke of Poor technique, Change solvent;
brush or spray gun visible fast-evaporating keep spray passes
after paint dries solvent, surface uniform, and
too hot paint before steel
temperature peaks
each day.
TABLE 14.1 Common Coating Failures, Their Causes, and Remedies [3]