Page 79 - Corrosion Engineering Principles and Practice
P. 79
58 C h a p t e r 4 C o r r o s i o n T h e r m o d y n a m i c s 59
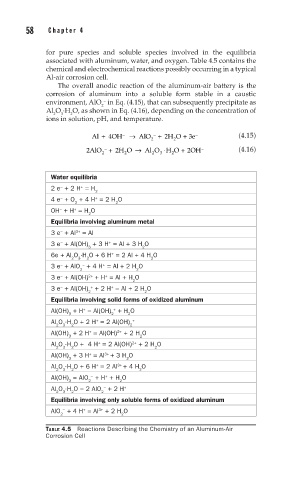
for pure species and soluble species involved in the equilibria
associated with aluminum, water, and oxygen. Table 4.5 contains the
chemical and electrochemical reactions possibly occurring in a typical
Al-air corrosion cell.
The overall anodic reaction of the aluminum-air battery is the
corrosion of aluminum into a soluble form stable in a caustic
−
environment, AlO in Eq. (4.15), that can subsequently precipitate as
2
Al O ·H O, as shown in Eq. (4.16), depending on the concentration of
2
3
2
ions in solution, pH, and temperature.
Al + 4OH − → AlO 2 − + 2H O + 3e (4.15)
−
2
−
⋅
2AlO 2 − + 2H O → Al O H O + 2OH (4.16)
3
2
2
2
Water equilibria
2 e + 2 H = H
−
+
2
4 e + O + 4 H = 2 H O
−
+
2 2
+
−
OH + H = H O
2
Equilibria involving aluminum metal
3 e + Al = Al
3+
−
3 e + Al(OH) + 3 H = Al + 3 H O
+
−
3 2
+
6e + Al O ·H O + 6 H = 2 Al + 4 H O
2 3 2 2
3 e + AlO + 4 H = Al + 2 H O
+
−
−
2 2
−
3 e + Al(OH) + H = Al + H O
2+
+
2
3 e + Al(OH) + 2 H = Al + 2 H O
+
−
+
2 2
Equilibria involving solid forms of oxidized aluminum
Al(OH) + H = Al(OH) + H O
+
+
3 2 2
+
Al O ·H O + 2 H = 2 Al(OH) +
2 3 2 2
2+
+
Al(OH) + 2 H = Al(OH) + 2 H O
3 2
Al O ·H O + 4 H = 2 Al(OH) + 2 H O
+
2+
2 3 2 2
Al(OH) + 3 H = Al + 3 H O
3+
+
3 2
3+
+
Al O ·H O + 6 H = 2 Al + 4 H O
2 3 2 2
−
Al(OH) = AlO + H + H O
+
3 2 2
Al O ·H O = 2 AlO + 2 H +
−
2 3 2 2
Equilibria involving only soluble forms of oxidized aluminum
−
AlO + 4 H = Al + 2 H O
3+
+
2 2
TABLE 4.5 Reactions Describing the Chemistry of an Aluminum-Air
Corrosion Cell