Page 101 - Coulson Richardson's Chemical Engineering Vol.6 Chemical Engineering Design 4th Edition
P. 101
84
100
90 Range CHEMICAL ENGINEERING
Isentropic efficiency 80
70
60
1 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0
Compression ratio
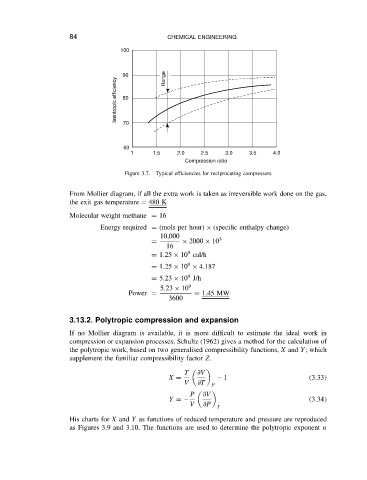
Figure 3.7. Typical efficiencies for reciprocating compressors
From Mollier diagram, if all the extra work is taken as irreversible work done on the gas,
the exit gas temperature D 480 K
Molecular weight methane D 16
Energy required D (mols per hour) ð (specific enthalpy change)
10,000
D ð 2000 ð 10 3
16
9
D 1.25 ð 10 cal/h
9
D 1.25 ð 10 ð 4.187
9
D 5.23 ð 10 J/h
5.23 ð 10 9
Power D D 1.45 MW
3600
3.13.2. Polytropic compression and expansion
If no Mollier diagram is available, it is more difficult to estimate the ideal work in
compression or expansion processes. Schultz (1962) gives a method for the calculation of
the polytropic work, based on two generalised compressibility functions, X and Y;which
supplement the familiar compressibility factor Z.
T ∂V
X D 1 3.33
V ∂T
P
P ∂V
Y D 3.34
V ∂P
T
His charts for X and Y as functions of reduced temperature and pressure are reproduced
as Figures 3.9 and 3.10. The functions are used to determine the polytropic exponent n