Page 704 - Discrete Mathematics and Its Applications
P. 704
10.4 Connectivity 683
Sometimes the removal from a graph of a vertex and all incident edges produces a subgraph
with more connected components. Such vertices are called cut vertices (or articulation points).
The removal of a cut vertex from a connected graph produces a subgraph that is not connected.
Analogously, an edge whose removal produces a graph with more connected components than
in the original graph is called a cut edge or bridge. Note that in a graph representing a computer
network, a cut vertex and a cut edge represent an essential router and an essential link that cannot
fail for all computers to be able to communicate.
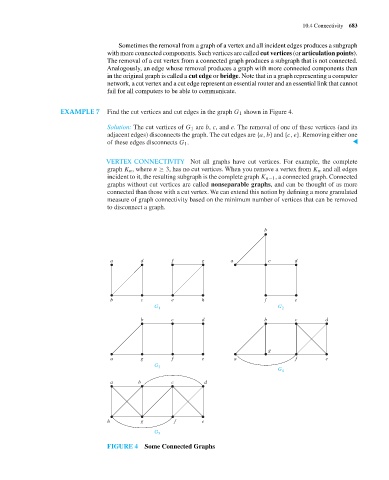
EXAMPLE 7 Find the cut vertices and cut edges in the graph G 1 shown in Figure 4.
Solution: The cut vertices of G 1 are b, c, and e. The removal of one of these vertices (and its
adjacent edges) disconnects the graph. The cut edges are {a, b} and {c, e}. Removing either one
of these edges disconnects G 1 . ▲
VERTEX CONNECTIVITY Not all graphs have cut vertices. For example, the complete
graph K n , where n ≥ 3, has no cut vertices. When you remove a vertex from K n and all edges
incident to it, the resulting subgraph is the complete graph K n−1 , a connected graph. Connected
graphs without cut vertices are called nonseparable graphs, and can be thought of as more
connected than those with a cut vertex. We can extend this notion by defining a more granulated
measure of graph connectivity based on the minimum number of vertices that can be removed
to disconnect a graph.
b
a d f g a c d
b c e h f e
G 1 G 2
b c d b c d
g
a g f e a f e
G 3
G 4
a b c d
h g f e
G 5
FIGURE 4 Some Connected Graphs