Page 148 -
P. 148
3:16 Page 111
2011/6/1
HAN
10-ch03-083-124-9780123814791
#29
3.5 Data Transformation and Data Discretization 111
D
branch C
B
A
home
entertainment 568
item_type computer 750
phone
150
security 50
2008 2009 2010
year
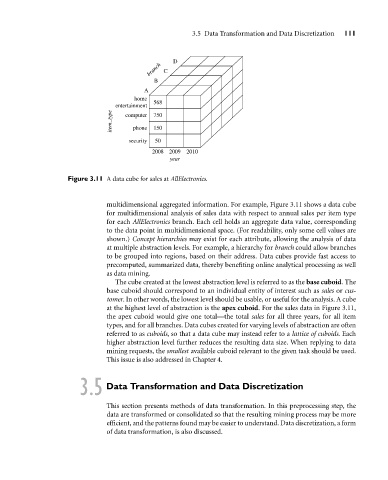
Figure 3.11 A data cube for sales at AllElectronics.
multidimensional aggregated information. For example, Figure 3.11 shows a data cube
for multidimensional analysis of sales data with respect to annual sales per item type
for each AllElectronics branch. Each cell holds an aggregate data value, corresponding
to the data point in multidimensional space. (For readability, only some cell values are
shown.) Concept hierarchies may exist for each attribute, allowing the analysis of data
at multiple abstraction levels. For example, a hierarchy for branch could allow branches
to be grouped into regions, based on their address. Data cubes provide fast access to
precomputed, summarized data, thereby benefiting online analytical processing as well
as data mining.
The cube created at the lowest abstraction level is referred to as the base cuboid. The
base cuboid should correspond to an individual entity of interest such as sales or cus-
tomer. In other words, the lowest level should be usable, or useful for the analysis. A cube
at the highest level of abstraction is the apex cuboid. For the sales data in Figure 3.11,
the apex cuboid would give one total—the total sales for all three years, for all item
types, and for all branches. Data cubes created for varying levels of abstraction are often
referred to as cuboids, so that a data cube may instead refer to a lattice of cuboids. Each
higher abstraction level further reduces the resulting data size. When replying to data
mining requests, the smallest available cuboid relevant to the given task should be used.
This issue is also addressed in Chapter 4.
3.5 Data Transformation and Data Discretization
This section presents methods of data transformation. In this preprocessing step, the
data are transformed or consolidated so that the resulting mining process may be more
efficient, and the patterns found may be easier to understand. Data discretization, a form
of data transformation, is also discussed.