Page 137 - Decision Making Applications in Modern Power Systems
P. 137
102 Decision Making Applications in Modern Power Systems
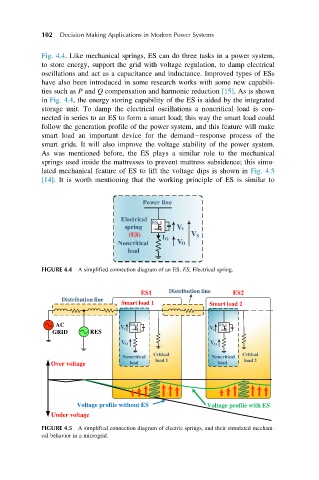
Fig. 4.4. Like mechanical springs, ES can do three tasks in a power system,
to store energy, support the grid with voltage regulation, to damp electrical
oscillations and act as a capacitance and inductance. Improved types of ESs
have also been introduced in some research works with some new capabili-
ties such as P and Q compensation and harmonic reduction [15]. As is shown
in Fig. 4.4, the energy storing capability of the ES is aided by the integrated
storage unit. To damp the electrical oscillations a noncritical load is con-
nected in series to an ES to form a smart load; this way the smart load could
follow the generation profile of the power system, and this feature will make
smart load an important device for the demand response process of the
smart grids. It will also improve the voltage stability of the power system.
As was mentioned before, the ES plays a similar role to the mechanical
springs used inside the mattresses to prevent mattress subsidence; this simu-
lated mechanical feature of ES to lift the voltage dips is shown in Fig. 4.5
[14]. It is worth mentioning that the working principle of ES is similar to
Power line
Electrical
ES
spring e V
(ES) V S
I O
Noncritical V O
load
FIGURE 4.4 A simplified connection diagram of an ES. ES, Electrical spring.
ES1 Distribution line ES2
Distribution line
Smart load 1 Smart load 2
AC ES ES
V e V e
GRID RES
V O V O
Critical Critical
Noncritical Noncritical
Over voltage load load 1 load load 2
Voltage profile without ES Voltage profile with ES
Under voltage
FIGURE 4.5 A simplified connection diagram of electric springs, and their simulated mechani-
cal behavior in a microgrid.