Page 149 - Decision Making Applications in Modern Power Systems
P. 149
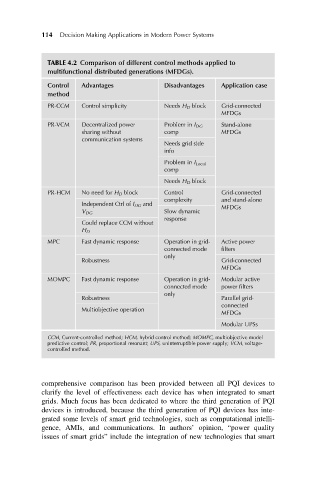
114 Decision Making Applications in Modern Power Systems
TABLE 4.2 Comparison of different control methods applied to
multifunctional distributed generations (MFDGs).
Control Advantages Disadvantages Application case
method
PR-CCM Control simplicity Needs H D block Grid-connected
MFDGs
PR-VCM Decentralized power Problem in I DG Stand-alone
sharing without comp MFDGs
communication systems
Needs grid side
info
Problem in I Local
comp
Needs H D block
PR-HCM No need for H D block Control Grid-connected
complexity and stand-alone
Independent Ctrl of I DG and MFDGs
V DG Slow dynamic
response
Could replace CCM without
H D
MPC Fast dynamic response Operation in grid- Active power
connected mode filters
only
Robustness Grid-connected
MFDGs
MOMPC Fast dynamic response Operation in grid- Modular active
connected mode power filters
only
Robustness Parallel grid-
connected
Multiobjective operation
MFDGs
Modular UPSs
CCM, Current-controlled method; HCM, hybrid control method; MOMPC, multiobjective model
predictive control; PR, proportional resonant; UPS, uninterruptible power supply; VCM, voltage-
controlled method.
comprehensive comparison has been provided between all PQI devices to
clarify the level of effectiveness each device has when integrated to smart
grids. Much focus has been dedicated to where the third generation of PQI
devices is introduced, because the third generation of PQI devices has inte-
grated some levels of smart grid technologies, such as computational intelli-
gence, AMIs, and communications. In authors’ opinion, “power quality
issues of smart grids” include the integration of new technologies that smart