Page 438 - Decision Making Applications in Modern Power Systems
P. 438
Impact of demand-side management system Chapter | 15 397
building load includes DC appliances, such as the brushless DC fans, DC
tube lights, and LED bulbs. Moreover, there are five DC bulbs used to make
the simulator of deferrable and cycle-based load. The simulators of the wash-
ing machine and the water pump are in the parallel combination of two DC
bulbs of 40 W, while one DC bulb of 60 W is used to design the simulator
of the refrigerator. The specifications of the microgrid components, such as
appliances, PV plant, ES, and SCCs, can be found in Table 15.3. The consid-
ered location of the appliances can be found in Table 15.4. The manual
switches are used to manually switch “ON”/“OFF” the appliance. Two speed
regulators are used to control the speed of the ceiling fans. The building load
is supplied by the PV plant and the BB. The ES consists of two BBs, BB-1
and BB-2, while the BB is the parallel combination of two batteries. The PV
plant consists of two arrays, and each array is the parallel combination of
four modules of 100 W each.
15.4.3 Control and monitoring unit of DC microgrid
The layout of the control and monitoring unit of the DC microgrid is shown
in Fig. 15.3. It consists of five boards. The board-1 consists of a microcon-
troller (Arduino mega), real-time clock, SD card reader, and power supply,
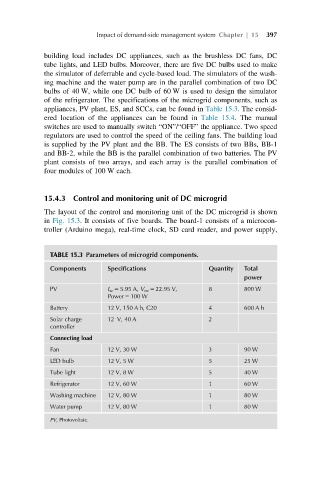
TABLE 15.3 Parameters of microgrid components.
Components Specifications Quantity Total
power
PV I sc 5 5.95 A, V oc 5 22.95 V, 8 800 W
Power 5 100 W
Battery 12 V, 150 A h, C20 4 600 A h
Solar charge 12 V, 40 A 2
controller
Connecting load
Fan 12 V, 30 W 3 90 W
LED bulb 12 V, 5 W 5 25 W
Tube light 12 V, 8 W 5 40 W
Refrigerator 12 V, 60 W 1 60 W
Washing machine 12 V, 80 W 1 80 W
Water pump 12 V, 80 W 1 80 W
PV, Photovoltaic.