Page 500 - Decision Making Applications in Modern Power Systems
P. 500
460 Decision Making Applications in Modern Power Systems
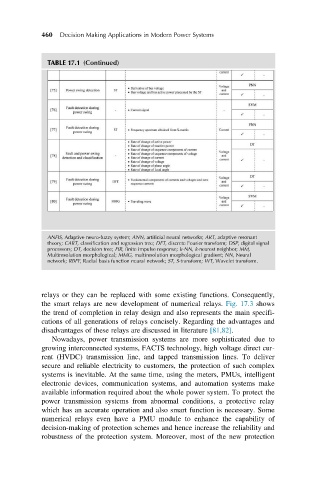
TABLE 17.1 (Continued)
ANFIS, Adaptive neuro-fuzzy system; ANN, artificial neural networks; ART, adaptive resonant
theory; CART, classification and regression tree; DFT, discrete Fourier transform; DSP, digital signal
processors; DT, decision tree; FIR, finite impulse response; k-NN, k-nearest neighbor; MM,
Multiresolution morphological; MMG, multiresolution morphological gradient; NN, Neural
network; RBFF, Radial basis function neural network; ST, S-transform; WT, Wavelet transform.
relays or they can be replaced with some existing functions. Consequently,
the smart relays are new development of numerical relays. Fig. 17.3 shows
the trend of completion in relay design and also represents the main specifi-
cations of all generations of relays concisely. Regarding the advantages and
disadvantages of these relays are discussed in literature [81,82].
Nowadays, power transmission systems are more sophisticated due to
growing interconnected systems, FACTS technology, high voltage direct cur-
rent (HVDC) transmission line, and tapped transmission lines. To deliver
secure and reliable electricity to customers, the protection of such complex
systems is inevitable. At the same time, using the meters, PMUs, intelligent
electronic devices, communication systems, and automation systems make
available information required about the whole power system. To protect the
power transmission systems from abnormal conditions, a protective relay
which has an accurate operation and also smart function is necessary. Some
numerical relays even have a PMU module to enhance the capability of
decision-making of protection schemes and hence increase the reliability and
robustness of the protection system. Moreover, most of the new protection