Page 503 - Decision Making Applications in Modern Power Systems
P. 503
Pattern-recognition methods for decision-making Chapter | 17 463
The design of the new pattern-recognition-based function can be operated
in two ways:
1. Stand-alone functions that consist of independent classification or estima-
tion mechanism. In this type of function the input is a predetermined con-
structed feature vector, and the final decision made by the function does
not interact with other functions. For example, the smart fault locator
proposed in Ref. [3] is a stand-alone function, and the output of the loca-
tor only identifies the fault point in a transmission line to restore the
power system as soon as possible.
2. Integrated functions that are a part of other protection schemes. This type
of function can communicate with other functions to enhance the perfor-
mance of them. The input of integrated functions contains the output of
other protection functions, and/or the input is selected or activated by the
decision of other protection functions. Moreover, the output of integrated
functions can be used to improve the performance of other protection
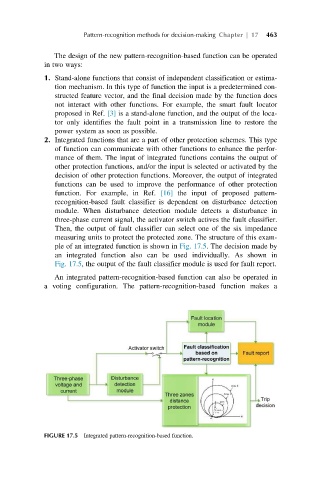
function. For example, in Ref. [16] the input of proposed pattern-
recognition-based fault classifier is dependent on disturbance detection
module. When disturbance detection module detects a disturbance in
three-phase current signal, the activator switch actives the fault classifier.
Then, the output of fault classifier can select one of the six impedance
measuring units to protect the protected zone. The structure of this exam-
ple of an integrated function is shown in Fig. 17.5. The decision made by
an integrated function also can be used individually. As shown in
Fig. 17.5, the output of the fault classifier module is used for fault report.
An integrated pattern-recognition-based function can also be operated in
a voting configuration. The pattern-recognition-based function makes a
FIGURE 17.5 Integrated pattern-recognition-based function.