Page 532 - Decision Making Applications in Modern Power Systems
P. 532
A reliable decision-making algorithm Chapter | 18 491
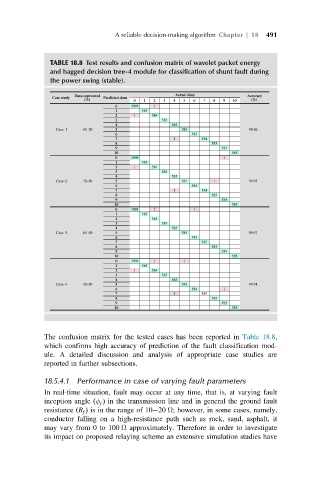
TABLE 18.8 Test results and confusion matrix of wavelet packet energy
and bagged decision tree-4 module for classification of shunt fault during
the power swing (stable).
Data segmented Actual class Accuracy
Case study Predicted class
(%) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 (%)
0 3999 1
1 585
2 1 584
3 585
4 585
Case–1 80–20 5 585 99.96
6 585
7 1 584
8 585
9 585
10 585
0 3999 1
1 585
2 1 584
3 585
4 585
Case–2 70–30 5 584 1 99.95
6 585
7 1 584
8 585
9 585
10 585
0 3998 1 1
1 585
2 585
3 585
4 585
Case–3 60–40 5 585 99.97
6 585
7 585
8 585
9 585
10 585
0 3998 1 1
1 585
2 1 584
3 585
4 585
Case–4 50–50 5 585 99.94
6 584 1
7 1 585
8 585
9 585
10 585
The confusion matrix for the tested cases has been reported in Table 18.8,
which confirms high accuracy of prediction of the fault classification mod-
ule. A detailed discussion and analysis of appropriate case studies are
reported in further subsections.
18.5.4.1 Performance in case of varying fault parameters
In real-time situation, fault may occur at any time, that is, at varying fault
inception angle ðφ Þ in the transmission line and in general the ground fault
f
resistance ðR f Þ is in the range of 10 20 Ω; however, in some cases, namely,
conductor falling on a high-resistance path such as rock, sand, asphalt, it
may vary from 0 to 100 Ω approximately. Therefore in order to investigate
its impact on proposed relaying scheme an extensive simulation studies have