Page 106 - Design for Environment A Guide to Sustainable Product Development
P. 106
Principles of Design for Envir onment 85
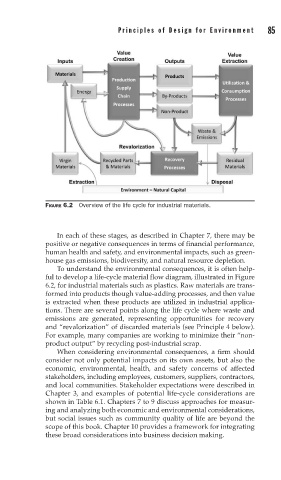
FIGURE 6.2 Overview of the life cycle for industrial materials.
In each of these stages, as described in Chapter 7, there may be
positive or negative consequences in terms of financial performance,
human health and safety, and environmental impacts, such as green-
house gas emissions, biodiversity, and natural resource depletion.
To understand the environmental consequences, it is often help-
ful to develop a life-cycle material flow diagram, illustrated in Figure
6.2, for industrial materials such as plastics. Raw materials are trans-
formed into products though value-adding processes, and then value
is extracted when these products are utilized in industrial applica-
tions. There are several points along the life cycle where waste and
emissions are generated, representing opportunities for recovery
and “revalorization” of discarded materials (see Principle 4 below).
For example, many companies are working to minimize their “non-
product output” by recycling post-industrial scrap.
When considering environmental consequences, a firm should
consider not only potential impacts on its own assets, but also the
economic, environmental, health, and safety concerns of affected
stakeholders, including employees, customers, suppliers, contractors,
and local communities. Stakeholder expectations were described in
Chapter 3, and examples of potential life-cycle considerations are
shown in Table 6.1. Chapters 7 to 9 discuss approaches for measur-
ing and analyzing both economic and environmental considerations,
but social issues such as community quality of life are beyond the
scope of this book. Chapter 10 provides a framework for integrating
these broad considerations into business decision making.