Page 107 - Design for Environment A Guide to Sustainable Product Development
P. 107
86 Cha pte r Six
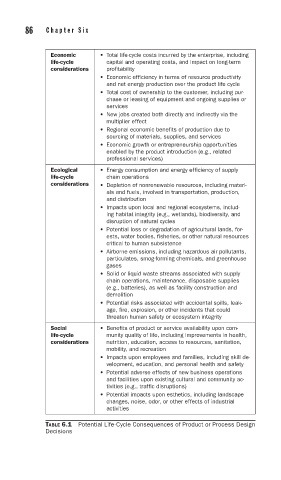
Economic • Total life-cycle costs incurred by the enterprise, including
life-cycle capital and operating costs, and impact on long-term
considerations profitability
• Economic efficiency in terms of resource productivity
and net energy production over the product life cycle
• Total cost of ownership to the customer, including pur-
chase or leasing of equipment and ongoing supplies or
services
• New jobs created both directly and indirectly via the
multiplier effect
• Regional economic benefits of production due to
sourcing of materials, supplies, and services
• Economic growth or entrepreneurship opportunities
enabled by the product introduction (e.g., related
professional services)
Ecological • Energy consumption and energy efficiency of supply
life-cycle chain operations
considerations • Depletion of nonrenewable resources, including materi-
als and fuels, involved in transportation, production,
and distribution
• Impacts upon local and regional ecosystems, includ-
ing habitat integrity (e.g., wetlands), biodiversity, and
disruption of natural cycles
• Potential loss or degradation of agricultural lands, for-
ests, water bodies, fisheries, or other natural resources
critical to human subsistence
• Airborne emissions, including hazardous air pollutants,
particulates, smog-forming chemicals, and greenhouse
gases
• Solid or liquid waste streams associated with supply
chain operations, maintenance, disposable supplies
(e.g., batteries), as well as facility construction and
demolition
• Potential risks associated with accidental spills, leak-
age, fire, explosion, or other incidents that could
threaten human safety or ecosystem integrity
Social • Benefits of product or service availability upon com-
life-cycle munity quality of life, including improvements in health,
considerations nutrition, education, access to resources, sanitation,
mobility, and recreation
• Impacts upon employees and families, including skill de-
velopment, education, and personal health and safety
• Potential adverse effects of new business operations
and facilities upon existing cultural and community ac-
tivities (e.g., traffic disruptions)
• Potential impacts upon esthetics, including landscape
changes, noise, odor, or other effects of industrial
activities
TABLE 6.1 Potential Life-Cycle Consequences of Product or Process Design
Decisions