Page 77 - Design for Environment A Guide to Sustainable Product Development
P. 77
56 Cha pte r F o u r
• Economic prosperity and continuity for the business and
its stakeholders,
• Social well-being and equity for both employees and
affected communities,
• Environmental protection and resource conservation, both
local and global.
This metaphor has been used as the basis for many sustainability
assessment tools including the GRI guidelines and the Dow Jones
Sustainability Indexes.
In the U.S., corporate environmental, health and safety excel-
lence has been the principal goal of the Global Environmental Man-
agement Initiative (GEMI), a consortium of over 40 multinational
companies that collaborate closely on codification of best practices
[8]. Since 1990, GEMI has developed and published a series of
studies that provide guidance to corporations on environmental
management practices, including climate and water strategies, per-
formance measurement, and supply chain management. The SD
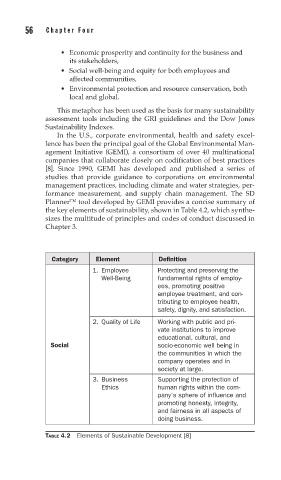
Planner™ tool developed by GEMI provides a concise summary of
the key elements of sustainability, shown in Table 4.2, which synthe-
sizes the multitude of principles and codes of conduct discussed in
Chapter 3.
Category Element Definition
1. Employee Protecting and preserving the
Well-Being fundamental rights of employ-
ees, promoting positive
employee treatment, and con-
tributing to employee health,
safety, dignity, and satisfaction.
2. Quality of Life Working with public and pri-
vate institutions to improve
educational, cultural, and
Social socio-economic well being in
the communities in which the
company operates and in
society at large.
3. Business Supporting the protection of
Ethics human rights within the com-
pany’s sphere of influence and
promoting honesty, integrity,
and fairness in all aspects of
doing business.
TABLE 4.2 Elements of Sustainable Development [8]