Page 217 - Design for Six Sigma a Roadmap for Product Development
P. 217
DFSS Transfer Function and Scorecards 189
Failure Modes
• …….
• ….
Noise Factors • ..
Piece-to-Piece Environmental Degradation Customer Usage Coupling
Signal Project Response FRs (DPs) Array
Factor (M) Scope
FR
DPs (PVs)
β
Ideal Function
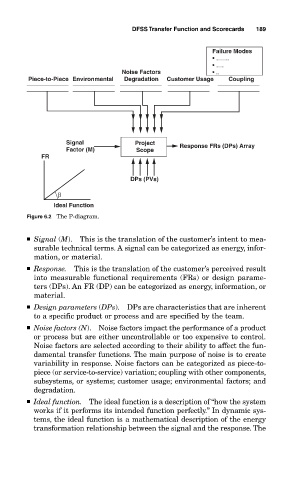
Figure 6.2 The P-diagram.
■ Signal (M). This is the translation of the customer’s intent to mea-
surable technical terms. A signal can be categorized as energy, infor-
mation, or material.
■ Response. This is the translation of the customer’s perceived result
into measurable functional requirements (FRs) or design parame-
ters (DPs). An FR (DP) can be categorized as energy, information, or
material.
■ Design parameters (DPs). DPs are characteristics that are inherent
to a specific product or process and are specified by the team.
■ Noise factors (N). Noise factors impact the performance of a product
or process but are either uncontrollable or too expensive to control.
Noise factors are selected according to their ability to affect the fun-
damental transfer functions. The main purpose of noise is to create
variability in response. Noise factors can be categorized as piece-to-
piece (or service-to-service) variation; coupling with other components,
subsystems, or systems; customer usage; environmental factors; and
degradation.
■ Ideal function. The ideal function is a description of “how the system
works if it performs its intended function perfectly.” In dynamic sys-
tems, the ideal function is a mathematical description of the energy
transformation relationship between the signal and the response. The