Page 362 - Design for Six Sigma a Roadmap for Product Development
P. 362
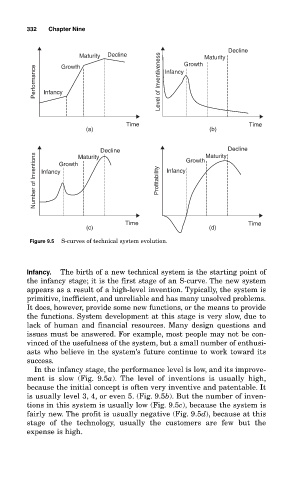
332 Chapter Nine
Decline
Maturity Decline Growth Maturity
Growth
Performance Infancy Level of Inventiveness Infancy
Time Time
(a) (b)
Decline Growth Maturity Decline
Number of Inventions Infancy Profitability Infancy
Maturity
Growth
Time Time
(c) (d)
Figure 9.5 S-curves of technical system evolution.
Infancy. The birth of a new technical system is the starting point of
the infancy stage; it is the first stage of an S-curve. The new system
appears as a result of a high-level invention. Typically, the system is
primitive, inefficient, and unreliable and has many unsolved problems.
It does, however, provide some new functions, or the means to provide
the functions. System development at this stage is very slow, due to
lack of human and financial resources. Many design questions and
issues must be answered. For example, most people may not be con-
vinced of the usefulness of the system, but a small number of enthusi-
asts who believe in the system’s future continue to work toward its
success.
In the infancy stage, the performance level is low, and its improve-
ment is slow (Fig. 9.5a). The level of inventions is usually high,
because the initial concept is often very inventive and patentable. It
is usually level 3, 4, or even 5. (Fig. 9.5b). But the number of inven-
tions in this system is usually low (Fig. 9.5c), because the system is
fairly new. The profit is usually negative (Fig. 9.5d), because at this
stage of the technology, usually the customers are few but the
expense is high.