Page 284 - Design of Reinforced Masonry Structures
P. 284
COLUMNS 5.5
5.2.2 Effective Column Height: Effects of End Restraints
The effective height, h, which appears in Euler’s formula for the buckling load of a column,
is valid only for a column with pin-ended supports, h being the distance between the pinned
ends. This formula must be modified if the end-restraint conditions are different from the
pin-ended conditions. This modification is easily done by considering the effective column
height Kh, defined as the distance between the inflection points on the buckled configura-
tion of the column, which depends on the end-restraint conditions. In order to account for
the effective column height, Eq. (5.3) can be expressed as Eq. (5.4) wherein Kh has been
substituted for h.
π 2 EA
P = (5.4)
cr 2
( Kh r / )
where K = the effective length factor whose value depends on the end restraint conditions.
It is important to recognize that the load-carrying capacity of a column is inversely pro-
portional to the square of the effective height as indicated by Eq. (5.4). Thus, determination
of effective height of a column is an important consideration in design. For a column with
pinned ends, value of the effective length factor K may be taken as unity (K = 1.0). Values
of K for other end-restraint conditions for columns, walls, and pilasters would be different.
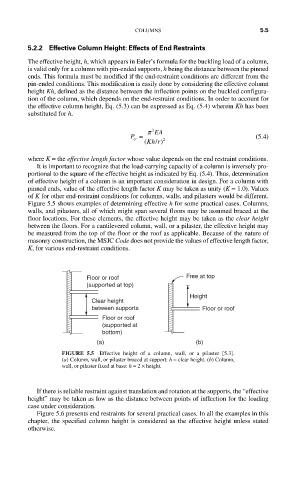
Figure 5.5 shows examples of determining effective h for some practical cases. Columns,
walls, and pilasters, all of which might span several floors may be assumed braced at the
floor locations. For these elements, the effective height may be taken as the clear height
between the floors. For a cantilevered column, wall, or a pilaster, the effective height may
be measured from the top of the floor or the roof as applicable. Because of the nature of
masonry construction, the MSJC Code does not provide the values of effective length factor,
K, for various end-restraint conditions.
Floor or roof Free at top
(supported at top)
Height
Clear height
between supports Floor or roof
Floor or roof
(supported at
bottom)
(a) (b)
FIGURE 5.5 Effective height of a column, wall, or a pilaster [5.3].
(a) Column, wall, or pilaster braced at support: h = clear height. (b) Column,
wall, or pilaster fixed at base: h = 2 × height.
If there is reliable restraint against translation and rotation at the supports, the “effective
height” may be taken as low as the distance between points of inflection for the loading
case under consideration.
Figure 5.6 presents end restraints for several practical cases. In all the examples in this
chapter, the specified column height is considered as the effective height unless stated
otherwise.