Page 311 - Design of Simple and Robust Process Plants
P. 311
8.3 Automation of Operation 297
± total automation
. A layered structure of operational states which have to be passed in defined
sequential order
. Defined transient operations to bring the process from one operational state
to the next.
. A set of detailed operational procedures
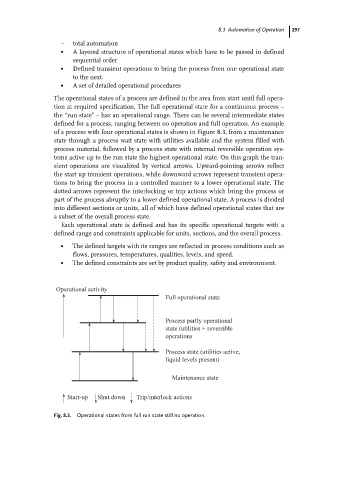
The operational states of a process are defined in the area from start until full opera-
tion at required specification. The full operational state for a continuous process ±
the ªrun stateº ± has an operational range. There can be several intermediate states
defined for a process, ranging between no operation and full operation. An example
of a process with four operational states is shown in Figure 8.3, from a maintenance
state through a process wait state with utilities available and the system filled with
process material, followed by a process state with internal reversible operation sys-
tems active up to the run state the highest operational state. On this graph the tran-
sient operations are visualized by vertical arrows. Upward-pointing arrows reflect
the start up transient operations, while downward arrows represent transient opera-
tions to bring the process in a controlled manner to a lower operational state. The
dotted arrows represent the interlocking or trip actions which bring the process or
part of the process abruptly to a lower defined operational state. A process is divided
into different sections or units, all of which have defined operational states that are
a subset of the overall process state.
Each operational state is defined and has its specific operational targets with a
defined range and constraints applicable for units, sections, and the overall process.
. The defined targets with its ranges are reflected in process conditions such as
flows, pressures, temperatures, qualities, levels, and speed.
. The defined constraints are set by product quality, safety and environment.
Operational activity
Full operational state
Process partly operational
state (utilities + reversible
operations
Process state (utilities active,
liquid levels present)
Maintenance state
Start-up Shut down Trip/interlock actions
Fig. 8.3. Operational states from full run state still no operation.