Page 400 - Design of Simple and Robust Process Plants
P. 400
9.6 Project Methodology for Operation Optimization 387
In the example of simple distillation, the qualities for top and bottom were sup-
posed to be manipulated by respectively reflux and vapor, while the levels were con-
trolled by distillate and bottom flows. This is just an assumption for this example; in
reality, the basic control configuration needs to be designed and the optimal pairing
for the control selected (see Chapter 8.)The top quality is seen as a fixed product
specification, a hard constraint, while the bottom specification is seen as a recycle
with an adjustable specification depending on plant economics. The pressure is con-
trolled by the cooling water.
The MBC is manipulating the set-point of the steam reboiler and the reflux flow
set-point for de-coupling of the interaction to achieve dual composition control as
self-optimizing controller.
The objective of floating pressure control might be implemented in the MBC sys-
tem, but may also be incorporated in the basic control layer (Shinskey, 1988).
The set-point of the feed flow might be set by three different sources:
1. Manual operator set-point for capacity.
2. MBC constrained capacity (maximization)-
3. OO constrained operation.
The set-point of the feed flow is a target of the MBC in case of feed maximization, as
far as the set-point is available and the constraint(s)have been defined. For instance,
floating capacity control to maximize the production under the day and night tem-
perature cycle, applicable if environmental (in)directly cooled exchangers are the
constraints. Also, the feed might be constrained by flooding to be identified by a
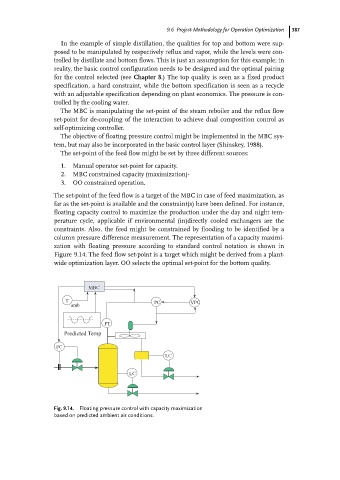
column pressure difference measurement. The representation of a capacity maximi-
zation with floating pressure according to standard control notation is shown in
Figure 9.14. The feed flow set-point is a target which might be derived from a plant-
wide optimization layer. OO selects the optimal set-point for the bottom quality.
MBC
T PC VPC
amb
PT
Predicted Temp
FC
LC
LC
Fig. 9.14. Floating pressure control with capacity maximization
based on predicted ambient air conditions.