Page 106 - Design of Solar Thermal Power Plants
P. 106
94 2. THE SOLAR RESOURCE AND METEOROLOGICAL PARAMETERS
It normally follows the tendency of degradation of annual global
irradiation along with latitude increase. In western areas, zonal
characteristics of the global radiation distribution may be concealed
by the major influences of geographic conditions that have appeared
in northern Xinjiang.
2. Features of topographic influences. The influences of topography on
global radiation distribution are mainly manifested in elevation
differences. In the QinghaieTibet Plateau, the mean elevation is
above 4000 m and is the strongest influence on annual solar
radiation distribution. According to the annual solar radiation
distribution chart, the QinghaieTibet Plateau has a high-value
center mainly caused by weakened absorption and scattering of the
atmosphere on solar radiation due to high elevation. The radiation
status at Tian Shan Mountain, Qilian Mountain, and other high
mountains is similar to that of the plateau. At the eastern margin of
the QinghaieTibet Plateau, due to rapid elevation change, global
radiation isolines are concentrated.
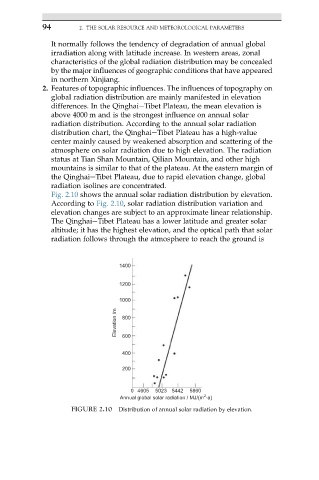
Fig. 2.10 shows the annual solar radiation distribution by elevation.
According to Fig. 2.10, solar radiation distribution variation and
elevation changes are subject to an approximate linear relationship.
The QinghaieTibet Plateau has a lower latitude and greater solar
altitude; it has the highest elevation, and the optical path that solar
radiation follows through the atmosphere to reach the ground is
1400
1200
1000
Elevation /m 800
600
400
200
0 4605 5023 5442 5860
2
Annual global solar radiation / MJ/(m ∙a)
FIGURE 2.10 Distribution of annual solar radiation by elevation.