Page 253 - Design of Solar Thermal Power Plants
P. 253
236 4. DESIGN OF THE CONCENTRATION SYSTEM
Rs x
y
y
x
z
z
Conic generatrix
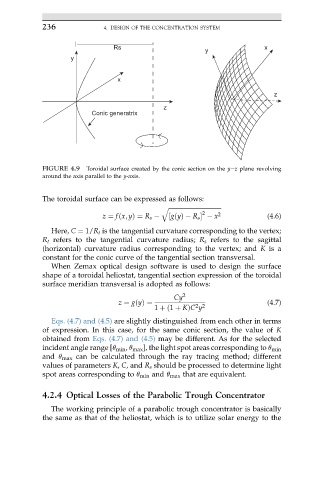
FIGURE 4.9 Toroidal surface created by the conic section on the yez plane revolving
around the axis parallel to the y-axis.
The toroidal surface can be expressed as follows:
q ffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffi
2 2
z ¼ fðx; yÞ¼ R s ½gðyÞ R s x (4.6)
Here, C ¼ 1/R t is the tangential curvature corresponding to the vertex;
R t refers to the tangential curvature radius; R s refers to the sagittal
(horizontal) curvature radius corresponding to the vertex; and K is a
constant for the conic curve of the tangential section transversal.
When Zemax optical design software is used to design the surface
shape of a toroidal heliostat, tangential section expression of the toroidal
surface meridian transversal is adopted as follows:
Cy 2
z ¼ gðyÞ¼ (4.7)
2 2
1 þð1 þ KÞC y
Eqs. (4.7) and (4.5) are slightly distinguished from each other in terms
of expression. In this case, for the same conic section, the value of K
obtained from Eqs. (4.7) and (4.5) may be different. As for the selected
incident angle range [q min , q max ], the light spot areas corresponding to q min
and q max can be calculated through the ray tracing method; different
values of parameters K, C, and R s should be processed to determine light
spot areas corresponding to q min and q max that are equivalent.
4.2.4 Optical Losses of the Parabolic Trough Concentrator
The working principle of a parabolic trough concentrator is basically
the same as that of the heliostat, which is to utilize solar energy to the