Page 189 - Designing Autonomous Mobile Robots : Inside the Mindo f an Intellegent Machine
P. 189
Chapter 12
Table
Steps
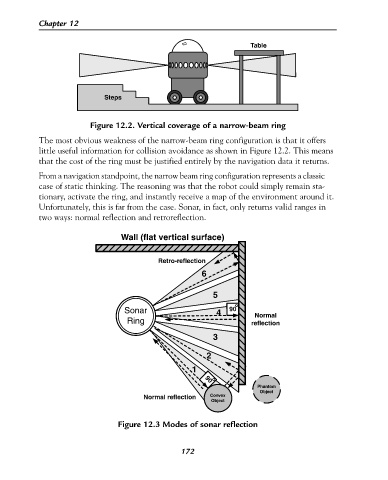
Figure 12.2. Vertical coverage of a narrow-beam ring
The most obvious weakness of the narrow-beam ring configuration is that it offers
little useful information for collision avoidance as shown in Figure 12.2. This means
that the cost of the ring must be justified entirely by the navigation data it returns.
From a navigation standpoint, the narrow beam ring configuration represents a classic
case of static thinking. The reasoning was that the robot could simply remain sta-
tionary, activate the ring, and instantly receive a map of the environment around it.
Unfortunately, this is far from the case. Sonar, in fact, only returns valid ranges in
two ways: normal reflection and retroreflection.
Wall (flat vertical surface)
Retro-reflection
6
5
o
Sonar 4 90
Normal
Ring reflection
3
2
1
o
90
Phantom
Object
Normal reflection Convex
Object
Figure 12.3 Modes of sonar reflection
172