Page 175 - Digital Analysis of Remotely Sensed Imagery
P. 175
140 Cha pte r F o u r
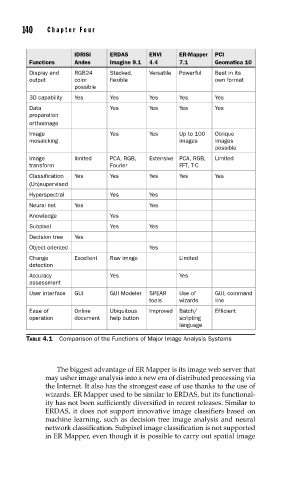
IDRISI ERDAS ENVI ER-Mapper PCI
Functions Andes Imagine 9.1 4.4 7.1 Geomatica 10
Display and RGB24 Stacked, Versatile Powerful Best in its
output color flexible own format
possible
3D capability Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Data Yes Yes Yes Yes
preparation
orthoimage
Image Yes Yes Up to 100 Oblique
mosaicking images images
possible
Image limited PCA, RGB, Extensive PCA, RGB, Limited
transform Fourier FFT, T-C
Classification Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
(Un)supervised
Hyperspectral Yes Yes
Neural net Yes Yes
Knowledge Yes
Subpixel Yes Yes
Decision tree Yes
Object oriented Yes
Change Excellent Raw image Limited
detection
Accuracy Yes Yes
assessment
User interface GUI GUI Modeler SPEAR Use of GUI, command
tools wizards line
Ease of Online Ubiquitous Improved Batch/ Efficient
operation document help button scripting
language
TABLE 4.1 Comparison of the Functions of Major Image Analysis Systems
The biggest advantage of ER Mapper is its image web server that
may usher image analysis into a new era of distributed processing via
the Internet. It also has the strongest ease of use thanks to the use of
wizards. ER Mapper used to be similar to ERDAS, but its functional-
ity has not been sufficiently diversified in recent releases. Similar to
ERDAS, it does not support innovative image classifiers based on
machine learning, such as decision tree image analysis and neural
network classification. Subpixel image classification is not supported
in ER Mapper, even though it is possible to carry out spatial image