Page 168 - Distillation theory
P. 168
P1: JPJ/FFX P2: FCH/FFX QC: FCH/FFX T1: FCH
0521820928c05 CB644-Petlyuk-v1 June 11, 2004 20:15
142 Distillation Trajectories and Conditions of Mixture Separability
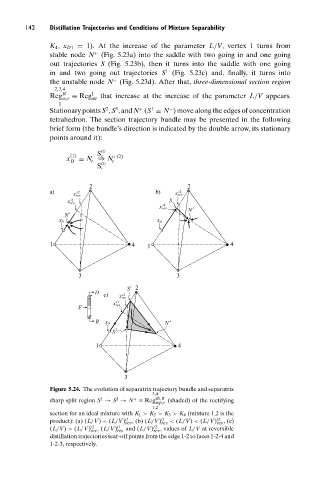
K 4 , x D1 = 1). At the increase of the parameter L/V, vertex 1 turns from
stable node N + (Fig. 5.23a) into the saddle with two going in and one going
out trajectories S (Fig. 5.23b), then it turns into the saddle with one going
1
in and two going out trajectories S (Fig. 5.23c) and, finally, it turns into
−
the unstable node N (Fig. 5.23d). After that, three-dimensional section region
2,3,4
Reg R ≡ Reg 1 that increase at the increase of the parameter L/V appears.
w,r att
1
3
2
1
Stationary points S , S , and N (S ≡ N ) move along the edges of concentration
−
+
tetrahedron. The section trajectory bundle may be presented in the following
brief form (the bundle’s direction is indicated by the double arrow, its stationary
points around it):
(2)
(1) S r +(2)
x ≡ N ⇒ N
−
D r r
(3)
S r
2 2
a) x rev 2 t b) x rev 2 t
x rev 1 t S
1 t
x rev +
+ N
N
x D x D
1 4 1 4
3 3
S 1 2
D
c) x 2 t
rev
x 1 t
F rev
B x D N +
S 2
1 4
3
Figure 5.24. The evolution of separatrix trajectory bundle and separatrix
3,4
1
2
+
sharp split region S → S → N ≡ Reg sh,R (shaded) of the rectifying
sep,r
1,2
section for an ideal mixture with K 1 > K 2 > K 3 > K 4 (mixture 1,2 is the
product): (a) (L/V) < (L/V) t1 , (b) (L/V) t1 < (L/V) < (L/V) t2 , (c)
rev
rev
rev
(L/V) > (L/V) t2 .(L/V) t1 and (L/V) t2 , values of L/V at reversible
rev
rev
rev
distillation trajectories tear-off points from the edge 1-2 to faces 1-2-4 and
1-2-3, respectively.