Page 172 - Distillation theory
P. 172
P1: JPJ/FFX P2: FCH/FFX QC: FCH/FFX T1: FCH
0521820928c05 CB644-Petlyuk-v1 June 11, 2004 20:15
146 Distillation Trajectories and Conditions of Mixture Separability
D
2 D 2
3
S
F a) b) S 1
α F
23 t2
B x rev
B
t1
x
+(1) rev
N x
x B
D 2
S
1 4 1 α 4
13
− +
N α N 2(α)
23 S x branch
α rev
13 13 13
3 2 3 N +(2)
D
F c)
B
x B
N +
t
x
1 rev 4
S 1
13
3
2,3,4
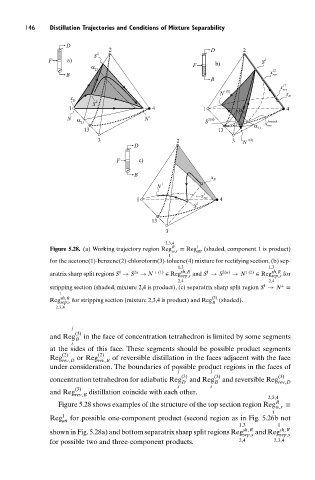
Figure 5.28. (a) Working trajectory region Reg R w,r ≡ Reg 1 att (shaded, component 1 is product)
1
for the acetone(1)-benzene(2)-chloroform(3)-toluene(4) mixture for rectifying section, (b) sep-
1,3 1,3
1
1
aratrix sharp split regions S → S 2α → N + (1) ∈ Reg sh,R and S → S 2(α) → N +(2) ∈ Reg sh,R for
sep,s
sep,s
2,4 2,4
1 +
stripping section (shaded, mixture 2,4 is product), (c) separatrix sharp split region S → N ≡
1
Reg sh,R for stripping section (mixture 2,3,4 is product) and Reg (3) (shaded).
B
sep,s
2,3,4
j
(3)
and Reg B in the face of concentration tetrahedron is limited by some segments
i
at the sides of this face. These segments should be possible product segments
(2) (2)
Reg or Reg of reversible distillation in the faces adjacent with the face
rev,D rev,B
under consideration. The boundaries of possible product regions in the faces of
j j
(3) (3) (3)
concentration tetrahedron for adiabatic Reg and Reg and reversible Reg
D B rev,D
i i
(3)
and Reg distillation coincide with each other.
rev,B
2,3,4
Figure 5.28 shows examples of the structure of the top section region Reg R ≡
w,r
1
Reg 1 for possible one-component product (second region as in Fig. 5.26b not
att
1,3 1
shown in Fig. 5.28a) and bottom separatrix sharp split regions Reg sh,R and Reg sh,R
sep,s sep,s
for possible two and three-component products. 2,4 2,3,4