Page 36 - Distributed model predictive control for plant-wide systems
P. 36
10 Distributed Model Predictive Control for Plant-Wide Systems
control framework of less computational burden, high flexibility, and good error tolerance.
Using distribute predictive control, the future state information of each subsystem is able to
feed into its interacted subsystem-based MPC and then satisfy the versatile control objective,
e.g., large lag system, and more restrict control performance requirements.
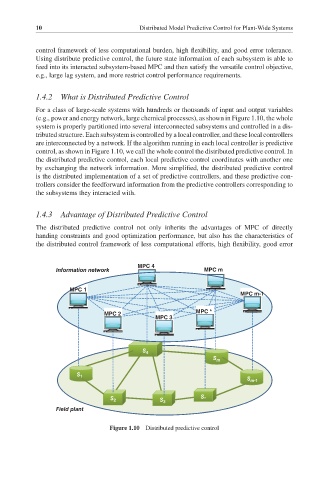
1.4.2 What is Distributed Predictive Control
For a class of large-scale systems with hundreds or thousands of input and output variables
(e.g., power and energy network, large chemical processes), as shown in Figure 1.10, the whole
system is properly partitioned into several interconnected subsystems and controlled in a dis-
tributed structure. Each subsystem is controlled by a local controller, and these local controllers
are interconnected by a network. If the algorithm running in each local controller is predictive
control, as shown in Figure 1.10, we call the whole control the distributed predictive control. In
the distributed predictive control, each local predictive control coordinates with another one
by exchanging the network information. More simplified, the distributed predictive control
is the distributed implementation of a set of predictive controllers, and these predictive con-
trollers consider the feedforward information from the predictive controllers corresponding to
the subsystems they interacted with.
1.4.3 Advantage of Distributed Predictive Control
The distributed predictive control not only inherits the advantages of MPC of directly
handing constraints and good optimization performance, but also has the characteristics of
the distributed control framework of less computational efforts, high flexibility, good error
MPC 4
Information network MPC m
MPC 1
MPC m-1
MPC 2 MPC *
MPC 3
S 4
S m
S 1
S m-1
S 2 S 3 S *
Field plant
Figure 1.10 Distributed predictive control