Page 34 - Distributed model predictive control for plant-wide systems
P. 34
8 Distributed Model Predictive Control for Plant-Wide Systems
Steady economic optimization
Real-time optimization
sp sp sp sp sp
y 1 y 2 y 3 y m−1 y m
Network
Distributed
Cont 1 Cont 2 Cont 3 Cont m-1 Cont m control
y
u * y 1 u * y 2 u * y 3 u * m–1 m–1 u m
* y m
3
1
2
S *
Distributed
S Na system
S 1 S 2
S *
S 3 S Na-1
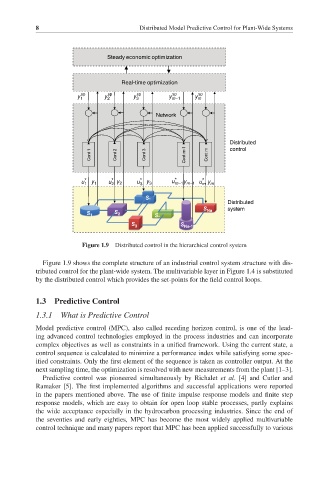
Figure 1.9 Distributed control in the hierarchical control system
Figure 1.9 shows the complete structure of an industrial control system structure with dis-
tributed control for the plant-wide system. The multivariable layer in Figure 1.4 is substituted
by the distributed control which provides the set-points for the field control loops.
1.3 Predictive Control
1.3.1 What is Predictive Control
Model predictive control (MPC), also called receding horizon control, is one of the lead-
ing advanced control technologies employed in the process industries and can incorporate
complex objectives as well as constraints in a unified framework. Using the current state, a
control sequence is calculated to minimize a performance index while satisfying some spec-
ified constraints. Only the first element of the sequence is taken as controller output. At the
next sampling time, the optimization is resolved with new measurements from the plant [1–3].
Predictive control was pioneered simultaneously by Richalet et al. [4] and Cutler and
Ramaker [5]. The first implemented algorithms and successful applications were reported
in the papers mentioned above. The use of finite impulse response models and finite step
response models, which are easy to obtain for open loop stable processes, partly explains
the wide acceptance especially in the hydrocarbon processing industries. Since the end of
the seventies and early eighties, MPC has become the most widely applied multivariable
control technique and many papers report that MPC has been applied successfully to various