Page 30 - Distributed model predictive control for plant-wide systems
P. 30
4 Distributed Model Predictive Control for Plant-Wide Systems
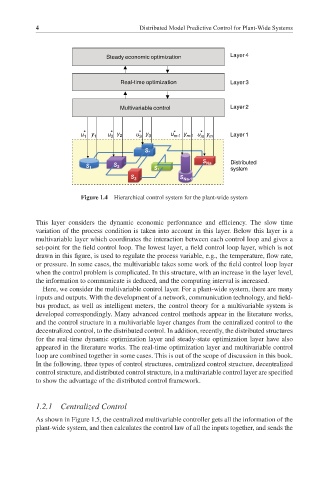
Steady economic optimization Layer 4
Real-time optimization Layer 3
Multivariable control Layer 2
* *
u 1 y 1 u 2 * y 2 u 3 * y 3 * u m-1 y m-1 u m y m Layer 1
S *
S Na Distributed
S 1 S 2
S * system
S 3 S Na-1
Figure 1.4 Hierarchical control system for the plant-wide system
This layer considers the dynamic economic performance and efficiency. The slow time
variation of the process condition is taken into account in this layer. Below this layer is a
multivariable layer which coordinates the interaction between each control loop and gives a
set-point for the field control loop. The lowest layer, a field control loop layer, which is not
drawn in this figure, is used to regulate the process variable, e.g., the temperature, flow rate,
or pressure. In some cases, the multivariable takes some work of the field control loop layer
when the control problem is complicated. In this structure, with an increase in the layer level,
the information to communicate is deduced, and the computing interval is increased.
Here, we consider the multivariable control layer. For a plant-wide system, there are many
inputs and outputs. With the development of a network, communication technology, and field-
bus product, as well as intelligent meters, the control theory for a multivariable system is
developed correspondingly. Many advanced control methods appear in the literature works,
and the control structure in a multivariable layer changes from the centralized control to the
decentralized control, to the distributed control. In addition, recently, the distributed structures
for the real-time dynamic optimization layer and steady-state optimization layer have also
appeared in the literature works. The real-time optimization layer and multivariable control
loop are combined together in some cases. This is out of the scope of discussion in this book.
In the following, three types of control structures, centralized control structure, decentralized
control structure, and distributed control structure, in a multivariable control layer are specified
to show the advantage of the distributed control framework.
1.2.1 Centralized Control
As shown in Figure 1.5, the centralized multivariable controller gets all the information of the
plant-wide system, and then calculates the control law of all the inputs together, and sends the