Page 445 - Dust Explosions in the Process Industries
P. 445
4 12 Dust Explosions in the Process Industries
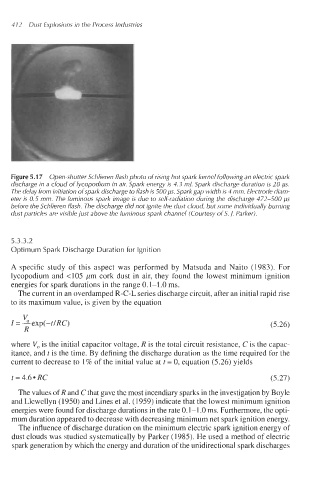
Figure 5.1 7 Open-shutter Schlieren flash photo of rising hot spark kernel following an electric spark
discharge in a cloud of lycopodium in air. Spark energy is 4.3 mJ. Spark discharge duration is 28 p.
The delay from initiation ofspark discharge to flash is 500 p. Spark gap width is 4 mm. Electrode diam-
eter is 0.5 mm. The luminous spark image is due to self-radiation during the discharge 472-500 p
before the Schlieren flash. The discharge did not ignite the dust cloud, but some individually burning
dust particles are visible just above the luminous spark channel (Courtesy of S. J. Parker).
5.3.3.2
Optimum Spark Discharge Duration for Ignition
A specific study of this aspect was performed by Matsuda and Naito (1983). For
lycopodium and <lo5 pm cork dust in air, they found the lowest minimum ignition
energies for spark durations in the range 0.1-1 .O ms.
The current in an overdamped R-C-L series discharge circuit, after an initial rapid rise
to its maximum value, is given by the equation
v,
I = -exp(-t/RC) (5.26)
R
where V, is the initial capacitor voltage, R is the total circuit resistance, C is the capac-
itance, and t is the time. By defining the discharge duration as the time required for the
current to decrease to 1% of the initial value at t = 0, equation (5.26) yields
t =4.6*RC (5.27)
The values of R and C that gave the most incendiary sparks in the investigation by Boyle
and Llewellyn (1950) and Lines et al. (1959) indicate that the lowest minimum ignition
energies were found for discharge durations in the rate 0.1-1 .0 ms. Furthermore, the opti-
mum duration appeared to decrease with decreasing minimum net spark ignition energy.
The influence of discharge duration on the minimum electric spark ignition energy of
dust clouds was studied systematically by Parker (1985). He used a method of electric
spark generation by which the energy and duration of the unidirectional spark discharges