Page 555 - Dust Explosions in the Process Industries
P. 555
522 Dust Explosions in the Process Industries
7.13.2.3
Nordtest Fire 01 1
The Nordtest (1989) method was designed specifically to meet the need of a reliable
bench-scale test for the minimum explosible concentration of dust clouds. The appara-
tus consists of three main parts:
A 15 liter explosion vessel with a dust dispersion system.
An ignition system.
A dust concentration measurement system.
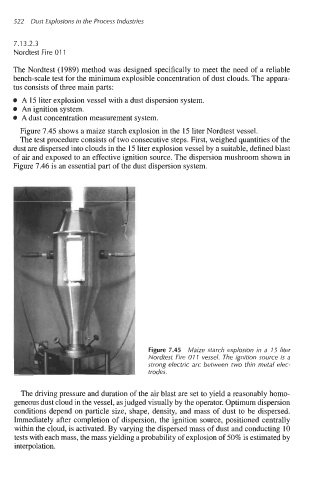
Figure 7.45 shows a maize starch explosion in the 15 liter Nordtest vessel.
The test procedure consists of two consecutive steps. First, weighed quantities of the
dust are dispersed into clouds in the 15 liter explosion vessel by a suitable, defined blast
of air and exposed to an effective ignition source. The dispersion mushroom shown in
Figure 7.46 is an essential part of the dust dispersion system.
Figure 7.45 Maize starch explosion in a 15 liter
Nordtest Fire 01 1 vessel. The ignition source is a
strong electric arc between two thin metal elec-
trodes.
The driving pressure and duration of the air blast are set to yield a reasonably homo-
geneous dust cloud in the vessel, as judged visually by the operator. Optimum dispersion
conditions depend on particle size, shape, density, and mass of dust to be dispersed.
Immediately after completion of dispersion, the ignition source, positioned centrally
within the cloud, is activated. By varying the dispersed mass of dust and conducting 10
tests with each mass, the mass yielding a probability of explosion of 50% is estimated by
interpolation.