Page 78 - Dynamic Vision for Perception and Control of Motion
P. 78
3 Subjects and Subject Classes
62
1. How to recognize members of classes of subjects.
2. Which type of reaction may be expected in the situation given. Biological
subjects, in general, have articulated bodies with some kind of elasticity or
plasticity. This may complicate visual recognition in a snapshot image. In
real life or in a video stream, typical motion sequences (even of only parts
of the body) may alleviate recognition considerably. Periodic motion of
limbs or other body parts is such an example. This will not be detailed here;
we concentrate on typical motion behaviors of vehicles as road traffic par-
ticipants, controlled by humans or by devices for automation.
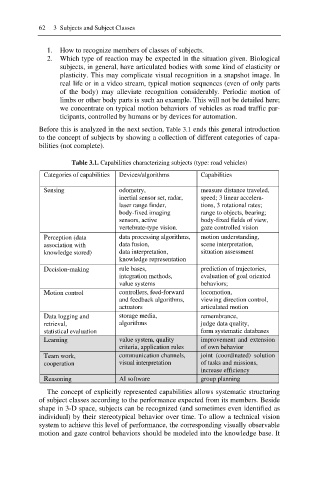
Before this is analyzed in the next section, Table 3.1 ends this general introduction
to the concept of subjects by showing a collection of different categories of capa-
bilities (not complete).
Table 3.1. Capabilities characterizing subjects (type: road vehicles)
Categories of capabilities Devices/algorithms Capabilities
Sensing odometry, measure distance traveled,
inertial sensor set, radar, speed; 3 linear accelera-
laser range finder, tions, 3 rotational rates;
body-fixed imaging range to objects, bearing;
sensors, active body-fixed fields of view,
vertebrate-type vision. gaze controlled vision
Perception (data data processing algorithms, motion understanding,
association with data fusion, scene interpretation,
knowledge stored) data interpretation, situation assessment
knowledge representation
Decision-making rule bases, prediction of trajectories,
integration methods, evaluation of goal oriented
value systems behaviors;
Motion control controllers, feed-forward locomotion,
and feedback algorithms, viewing direction control,
actuators articulated motion
Data logging and storage media, remembrance,
retrieval, algorithms judge data quality,
statistical evaluation form systematic databases
Learning value system, quality improvement and extension
criteria, application rules of own behavior
Team work, communication channels, joint (coordinated) solution
cooperation visual interpretation of tasks and missions,
increase efficiency
Reasoning AI software group planning
The concept of explicitly represented capabilities allows systematic structuring
of subject classes according to the performance expected from its members. Beside
shape in 3-D space, subjects can be recognized (and sometimes even identified as
individual) by their stereotypical behavior over time. To allow a technical vision
system to achieve this level of performance, the corresponding visually observable
motion and gaze control behaviors should be modeled into the knowledge base. It