Page 200 - Dynamics and Control of Nuclear Reactors
P. 200
198 CHAPTER 14 Pressurized heavy water reactors
Reactivity Control Mechanisms
To steam generators
Mechanical Control Absorbers (MCA)
Adjuster Rods (AR) Reactor
Liquid Zone Controllers (LZC)
Ion Plantinum
Chambers Detectors
Digital Control Algorithms Neutron flux
and
rate
Power
Reactor
Reactivity Control Error Power
Demand Power
Mechanisms Power Routine Measurement
Algorithms and Calibration
Thermal Power
Measurement
Reactor Power Setpoint
(From the operator in alternate mode)
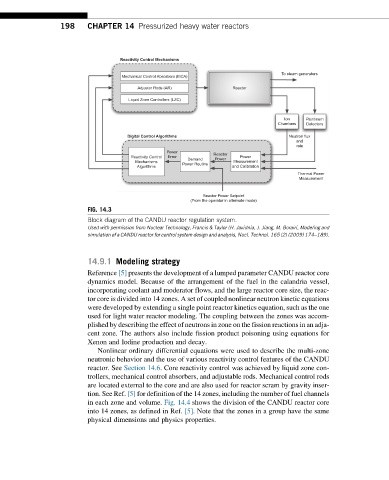
FIG. 14.3
Block diagram of the CANDU reactor regulation system.
Used with permission from Nuclear Technology, Francis & Taylor (H. Javidnia, J. Jiang, M. Borairi, Modeling and
simulation of a CANDU reactor for control system design and analysis, Nucl. Technol. 165 (2) (2009) 174–189).
14.9.1 Modeling strategy
Reference [5] presents the development of a lumped parameter CANDU reactor core
dynamics model. Because of the arrangement of the fuel in the calandria vessel,
incorporating coolant and moderator flows, and the large reactor core size, the reac-
tor core is divided into 14 zones. A set of coupled nonlinear neutron kinetic equations
were developed by extending a single point reactor kinetics equation, such as the one
used for light water reactor modeling. The coupling between the zones was accom-
plished by describing the effect of neutrons in zone on the fission reactions in an adja-
cent zone. The authors also include fission product poisoning using equations for
Xenon and Iodine production and decay.
Nonlinear ordinary differential equations were used to describe the multi-zone
neutronic behavior and the use of various reactivity control features of the CANDU
reactor. See Section 14.6. Core reactivity control was achieved by liquid zone con-
trollers, mechanical control absorbers, and adjustable rods. Mechanical control rods
are located external to the core and are also used for reactor scram by gravity inser-
tion. See Ref. [5] for definition of the 14 zones, including the number of fuel channels
in each zone and volume. Fig. 14.4 shows the division of the CANDU reactor core
into 14 zones, as defined in Ref. [5]. Note that the zones in a group have the same
physical dimensions and physics properties.