Page 113 - E-Bussiness and E-Commerce Management Strategy, Implementation, and Practice
P. 113
M02_CHAF9601_04_SE_C02.QXD:D01_CHAF7409_04_SE_C01.QXD 16/4/09 11:07 Page 80
80 Part 1 Introduction
1. Marketplace position 2. Revenue model 3. Commercial model
Y
Manufacturer or Direct product Fixed-price
primary service sales of sale
provider product or service
B B B A
Y Y
Reseller/retailer Subscription or Brokered or
(intermediary) rental of negotiated
service deal
A B
Y Y Y
Commission-based
Marketplace/exchange sales Auction or
(intermediary) (affiliate, auction, spot
marketplace)
A
Y Y
Media owner Advertising Product or service
or publisher (banner ads, bundling
(intermediary) sponsorship)
Supply chain Sales of syndicated Loyalty-based
provider content or services pricing or
or integrator (for media owner) promotions
Key
Not-for-profit Y = Yahoo!
organization
A = Amazon
B = Book publisher
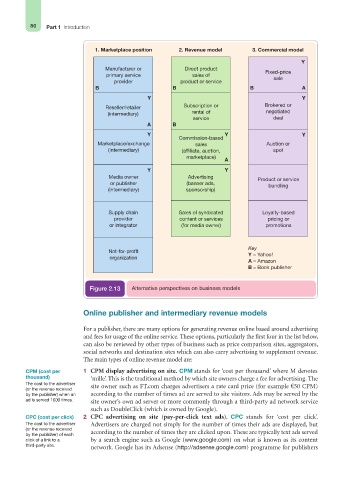
Figure 2.13 Alternative perspectives on business models
Online publisher and intermediary revenue models
For a publisher, there are many options for generating revenue online based around advertising
and fees for usage of the online service. These options, particularly the first four in the list below,
can also be reviewed by other types of business such as price comparison sites, aggregators,
social networks and destination sites which can also carry advertising to supplement revenue.
The main types of online revenue model are:
CPM (cost per 1 CPM display advertising on site. CPM stands for ‘cost per thousand’ where M denotes
thousand) ‘mille’. This is the traditional method by which site owners charge a fee for advertising. The
The cost to the advertiser
(or the revenue received site owner such as FT.com charges advertisers a rate card price (for example €50 CPM)
by the publisher) when an according to the number of times ad are served to site visitors. Ads may be served by the
ad is served 1000 times. site owner’s own ad server or more commonly through a third-party ad network service
such as DoubleClick (which is owned by Google).
CPC (cost per click) 2 CPC advertising on site (pay-per-click text ads). CPC stands for ‘cost per click’.
The cost to the advertiser Advertisers are charged not simply for the number of times their ads are displayed, but
(or the revenue received
by the publisher) of each according to the number of times they are clicked upon. These are typically text ads served
click of a link to a by a search engine such as Google (www.google.com) on what is known as its content
third-party site.
network. Google has its Adsense (http://adsense.google.com) programme for publishers