Page 266 - E-Bussiness and E-Commerce Management Strategy, Implementation, and Practice
P. 266
M04_CHAF9601_04_SE_C04.QXD:D01_CHAF7409_04_SE_C01.QXD 16/4/09 11:11 Page 233
Chapter 4 E-environment 233
THE e-ECONOMY
ENVIRONMENT MARKET POLITICAL INFRASTRUCTURAL
iEm • Educational Infrastructure iEp • Level of political leadership iEi • Infrastructure availability
• Level of IT skills • Enabling nature of legal • Infrastructure quality
• Supporting industries and regulatory environment
• Climate for innovation for e-commerce
• Cost of access
READINESS Citizen readiness Business readiness Government readiness
iRc • Measures of barriers to iRb • Measures of barriers to iRg • Awareness, leadership,
uptake (awareness, trust, uptake (awareness, trust, published strategies
skills, cost) skills, cost) • Level of coordination
• Penetration of access • Penetration of access • Systems readiness, back
devices devices office integration,
standardization
UPTAKE AND USE Citizen use Business use Government use
iUc • Level of basic use iUb • Level of basic use iUg • Level of basic use
• Ubiquity/fairness (including publication) (including publication)
of adoption • Ubiquity/fairness • Sophistication of use
• Sophistication of use of adoption
• Sophistication of use
IMPACT Citizen impact Business impact Government impact
iIc • Impact on ilb • Impact on ilg • Impact on
commerce/spending commerce/spending commerce/spending
• Impact on behaviour • Impact on service offering: • Impact on working practices
additional/enhanced services • Impact on costs/effiency
• Impact on working practices
• Impact on costs/effiency
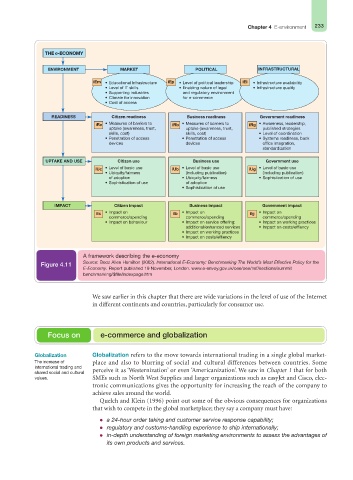
A framework describing the e-economy
Source: Booz Allen Hamilton (2002). International E-Economy: Benchmarking The World’s Most Effective Policy for the
Figure 4.11
E-Economy. Report published 19 November, London. www.e-envoy.gov.uk/oee/oee/nsf/sections/summit_
benchmarking/$file/indexpage.htm
We saw earlier in this chapter that there are wide variations in the level of use of the Internet
in different continents and countries, particularly for consumer use.
Focus on e-commerce and globalization
Globalization Globalization refers to the move towards international trading in a single global market-
The increase of place and also to blurring of social and cultural differences between countries. Some
international trading and
shared social and cultural perceive it as ‘Westernization’ or even ‘Americanization’. We saw in Chapter 1 that for both
values. SMEs such as North West Supplies and larger organizations such as easyJet and Cisco, elec-
tronic communications gives the opportunity for increasing the reach of the company to
achieve sales around the world.
Quelch and Klein (1996) point out some of the obvious consequences for organizations
that wish to compete in the global marketplace; they say a company must have:
a 24-hour order taking and customer service response capability;
regulatory and customs-handling experience to ship internationally;
in-depth understanding of foreign marketing environments to assess the advantages of
its own products and services.