Page 387 - Earth's Climate Past and Future
P. 387
Appendix 2
Isotopes of Carbon
13
12
Both C and C are stable (nonradioactive) isotopes of waters in some regions. For carbon that forms in the
13
carbon that occur naturally in Earth’s vegetation, water, absence of oxygen (in “reducing conditions”), δ C val-
and air. The C isotope accounts for more than 99% of ues can be far more negative, around –50 to –60‰.
12
13
all the carbon present on Earth, and C accounts for Carbon samples with relatively large amounts of C
13
12
13
most of the rest. A small amount exists as radioactive compared with C have more positive δ C values and
13
12
14 C. Geochemists who analyze material for its carbon are referred to as C-enriched or C-depleted. Sam-
13
isotope composition measure small variations around ples with relatively small amounts of C compared with
13
the average C/ C ratio of less than 0.01. 12 C have more negative δ C values and are referred to
13
12
12
13
Similar to the convention used for oxygen isotopes, as C-depleted or C-enriched.
13
12
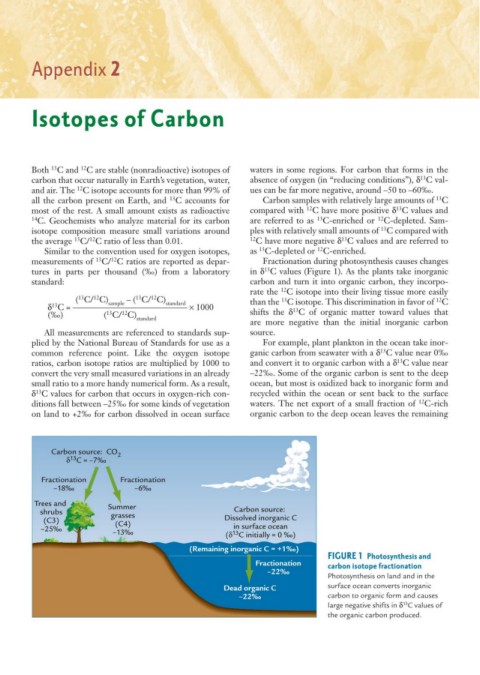
measurements of C/ C ratios are reported as depar- Fractionation during photosynthesis causes changes
13
tures in parts per thousand (‰) from a laboratory in δ C values (Figure 1). As the plants take inorganic
standard: carbon and turn it into organic carbon, they incorpo-
12
rate the C isotope into their living tissue more easily
12
13
12
13
( C/ C) sample – ( C/ C) standard than the C isotope. This discrimination in favor of C
12
13
δ C = –––––––––––––––––––––––––––––– × 1000 13
13
(‰) ( C/ C) shifts the δ C of organic matter toward values that
12
13
standard
are more negative than the initial inorganic carbon
All measurements are referenced to standards sup- source.
plied by the National Bureau of Standards for use as a For example, plant plankton in the ocean take inor-
13
common reference point. Like the oxygen isotope ganic carbon from seawater with a δ C value near 0‰
13
ratios, carbon isotope ratios are multiplied by 1000 to and convert it to organic carbon with a δ C value near
convert the very small measured variations in an already –22‰. Some of the organic carbon is sent to the deep
small ratio to a more handy numerical form. As a result, ocean, but most is oxidized back to inorganic form and
δ C values for carbon that occurs in oxygen-rich con- recycled within the ocean or sent back to the surface
13
12
ditions fall between –25‰ for some kinds of vegetation waters. The net export of a small fraction of C-rich
on land to +2‰ for carbon dissolved in ocean surface organic carbon to the deep ocean leaves the remaining
Carbon source: CO 2
13
δ C = –7‰
Fractionation Fractionation
–18‰ –6‰
Trees and Summer
shrubs grasses Carbon source:
(C3) (C4) Dissolved inorganic C
–25‰ in surface ocean
–13‰ (δ C initially = 0 ‰)
13
(Remaining inorganic C = +1‰)
FIGURE 1 Photosynthesis and
Fractionation carbon isotope fractionation
–22‰
Photosynthesis on land and in the
Dead organic C surface ocean converts inorganic
–22‰ carbon to organic form and causes
large negative shifts in δ C values of
13
the organic carbon produced.