Page 100 - Effective Communication Soft Skills Strategies For Success by Nitin Bhatnagar, Mamta Bhatnagar
P. 100
Project Name: Manual for Soft Skills
\\mtpdy01\Womat\Indesign\Bhatnagar-Manual for Soft skills\06-Pagination\06-A-Finals\06-AA-Appl\Bhatnagar_Chapter 05.indd
88 | Chapter 5 ACE Pro India Pvt. Ltd.
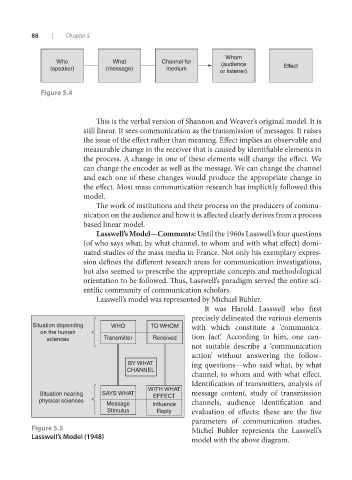
Whom
Who What Channel for (audience
(speaker) (message) medium or listener) Effect
Figure 5.4
This is the verbal version of Shannon and Weaver’s original model. It is
still linear. It sees communication as the transmission of messages. It raises
the issue of the effect rather than meaning. Effect implies an observable and
measurable change in the receiver that is caused by identifiable elements in
the process. A change in one of these elements will change the effect. We
can change the encoder as well as the message. We can change the channel
and each one of these changes would produce the appropriate change in
the effect. Most mass communication research has implicitly followed this
model.
The work of institutions and their process on the producers of commu-
nication on the audience and how it is affected clearly derives from a process
based linear model.
Lasswell’s Model—Comments: Until the 1960s Lasswell’s four questions
(of who says what, by what channel, to whom and with what effect) domi-
nated studies of the mass media in France. Not only his exemplary expres-
sion defines the different research areas for communication investigations,
but also seemed to prescribe the appropriate concepts and methodological
orientation to be followed. Thus, Lasswell’s paradigm served the entire sci-
entific community of communication scholars.
Lasswell’s model was represented by Michael Buhler.
It was Harold Lasswell who first
precisely delineated the various elements
Situation depending WHO TO WHOM with which constitute a ‘communica-
on the human
sciences Transmitter Received tion fact’. According to him, one can-
not suitable describe a ‘communication
action’ without answering the follow-
BY WHAT ing questions—who said what, by what
CHANNEL
channel, to whom and with what effect.
Identification of transmitters, analysis of
WITH WHAT
Situation nearing SAYS WHAT EFFECT message content, study of transmission
physical sciences Message Influence channels, audience identification and
Stimulus Reply evaluation of effects; these are the five
parameters of communication studies.
Figure 5.5 Michel Buhler represents the Lasswell’s
Lasswell’s Model (1948) model with the above diagram.
Bhatnagar_Chapter 05.indd 88 2011-06-23 7:56:05 PM
Modified Date: Thu, Jun 23, 2011 06:22:39 PM Output Date: Thu, Jun 23, 2011 07:56:03 PM
TEMPLATE Page Number: PB