Page 233 - Electrical Equipment Handbook _ Troubleshooting and Maintenance
P. 233
SYNCHRONOUS MACHINES
11.8 CHAPTER ELEVEN
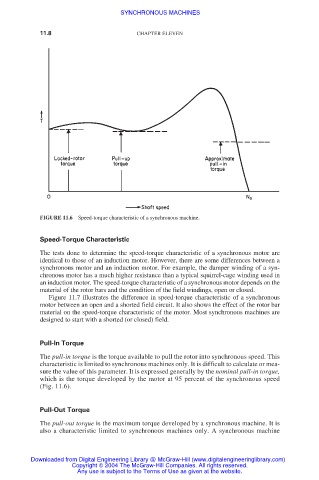
FIGURE 11.6 Speed-torque characteristic of a synchronous machine.
Speed-Torque Characteristic
The tests done to determine the speed-torque characteristic of a synchronous motor are
identical to those of an induction motor. However, there are some differences between a
synchronous motor and an induction motor. For example, the damper winding of a syn-
chronous motor has a much higher resistance than a typical squirrel-cage winding used in
an induction motor. The speed-torque characteristic of a synchronous motor depends on the
material of the rotor bars and the condition of the field windings, open or closed.
Figure 11.7 illustrates the difference in speed-torque characteristic of a synchronous
motor between an open and a shorted field circuit. It also shows the effect of the rotor bar
material on the speed-torque characteristic of the motor. Most synchronous machines are
designed to start with a shorted (or closed) field.
Pull-In Torque
The pull-in torque is the torque available to pull the rotor into synchronous speed. This
characteristic is limited to synchronous machines only. It is difficult to calculate or mea-
sure the value of this parameter. It is expressed generally by the nominal pull-in torque,
which is the torque developed by the motor at 95 percent of the synchronous speed
(Fig. 11.6).
Pull-Out Torque
The pull-out torque is the maximum torque developed by a synchronous machine. It is
also a characteristic limited to synchronous machines only. A synchronous machine
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.