Page 3 - Electrical Equipment Handbook _ Troubleshooting and Maintenance
P. 3
FUNDAMENTALS OF ELECTRIC SYSTEMS
1.2 CHAPTER ONE
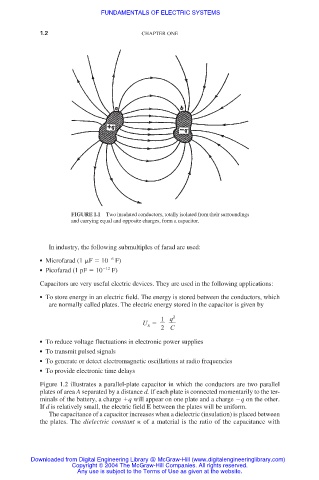
FIGURE 1.1 Two insulated conductors, totally isolated from their surroundings
and carrying equal and opposite charges, form a capacitor.
In industry, the following submultiples of farad are used:
● Microfarad (1 F 10 6 F)
● Picofarad (1 pF 10 12 F)
Capacitors are very useful electric devices. They are used in the following applications:
● To store energy in an electric field. The energy is stored between the conductors, which
are normally called plates. The electric energy stored in the capacitor is given by
1 q 2
U
E 2 C
● To reduce voltage fluctuations in electronic power supplies
● To transmit pulsed signals
● To generate or detect electromagnetic oscillations at radio frequencies
● To provide electronic time delays
Figure 1.2 illustrates a parallel-plate capacitor in which the conductors are two parallel
plates of area A separated by a distance d. If each plate is connected momentarily to the ter-
minals of the battery, a charge q will appear on one plate and a charge q on the other.
If d is relatively small, the electric field E between the plates will be uniform.
The capacitance of a capacitor increases when a dielectric (insulation) is placed between
the plates. The dielectric constant of a material is the ratio of the capacitance with
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.