Page 33 - Electrical Equipment Handbook _ Troubleshooting and Maintenance
P. 33
INTRODUCTION TO MACHINERY PRINCIPLES
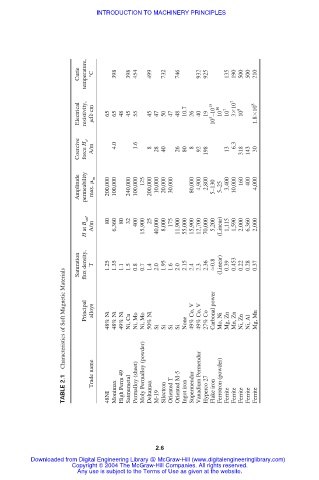
Curie temperature, °C 398 398 454 499 732 746 932 925 135 190 500 500 210
Electrical resistivity,
cm 65 65 48 45 55 45 47 50 47 48 10.7 26 40 19 10 5 –10 15 10 16 10 7 3 10 7 10 9 1.8 10 8
Coercive force H c , A/m 4.0 1.6 8 28 40 26 80 8 92 198 13 6.3 318 143 30
Amplitude permeability max. m 200,000 100,000 240,000 100,000 125 200,000 10,000 20,000 30,000 80,000 4,900 2,800 5–130 5–25 3,400 10,000 160 400 4,000
H at B sat , A/m 80 6,360 80 32 400 15,900 25 40,000 8,000 175 11,900 55,000 15,900 12,700 70,000 5,200 (Linear) 1,115 1,590 2,000 6,360 2,000
Saturation flux density, T 1.25 1.35 1.1 1.5 0.8 0.7 1.4 2.0 1.95 1.6 2.0 2.15 2.4 2.3 2.36 0.8 (Linear) 0.39 0.453 0.22 0.28 0.37
Characteristics of Soft Magnetic Materials Principal alloys 48% Ni 48% Ni 49% Ni Ni, Cu Ni, Mo Ni, Mo 50% Ni Si Si Si Si None 49% Co, V 49% Co, V 27% Co Carbonal power Mo, Ni Mg, Zn Mn, Zn Ni, Zn Ni, Al Mg, Mn
TABLE 2.1 Trade name 48NI Monimax High Perm 49 Satmumetal Permalloy (sheet) Moly Permalloy (powder) Deltamax M-19 Silectron Oriented T Oriented M-5 Ingot iron Supermendur Vanadium Permendur Hyperco 27 Flake iron Ferrotron (powder) Ferrite Ferrite Ferrite Ferrite Ferrite
2.6
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.