Page 47 - Electrical Equipment Handbook _ Troubleshooting and Maintenance
P. 47
TRANSFORMERS
3.4 CHAPTER THREE
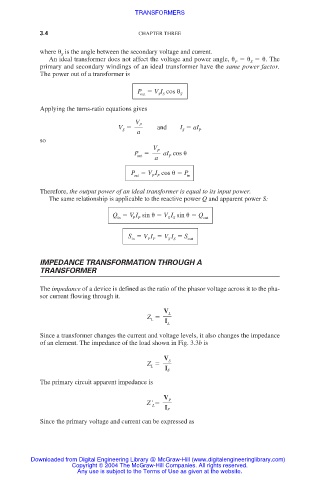
where is the angle between the secondary voltage and current.
S
An ideal transformer does not affect the voltage and power angle, . The
P
S
primary and secondary windings of an ideal transformer have the same power factor.
The power out of a transformer is
P V I cos
out S S S
Applying the turns-ratio equations gives
V
P
V and I aI P
S
S
a
so
V
P
P aI cos
P
out
a
P V I cos P
out P P in
Therefore, the output power of an ideal transformer is equal to its input power.
The same relationship is applicable to the reactive power Q and apparent power S:
Q V I sin V I sin Q
in P P S S out
S V I V I S out
P P
S S
in
IMPEDANCE TRANSFORMATION THROUGH A
TRANSFORMER
The impedance of a device is defined as the ratio of the phasor voltage across it to the pha-
sor current flowing through it.
V L
Z
L
I
L
Since a transformer changes the current and voltage levels, it also changes the impedance
of an element. The impedance of the load shown in Fig. 3.3b is
V
Z S
L
I S
The primary circuit apparent impedance is
V
Z ' P
L
I P
Since the primary voltage and current can be expressed as
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.