Page 192 - Electrical Installation in Hazardous Area
P. 192
156 Electrical installations in hazardous areas
may occur during the normal operation of the plant. Again, these are
synonymous in derivation with their gas and vapour counterparts and are
not expected to be present for more than 10 per cent of the time. Typical of
such releases are the interior of some process vessels and loading points,
and access doors to dust processing vessels or transport systems.
Secondary grade sources of release
Secondary Grade Sources of Release are those which are not normally
expected to release except in abnormal operation, such as the failure of
extract filters and similar situations.
6.2.2 Definition of Zones
Hazardous zones are related to the grade of release in much the same way
as in the gas or vapour situation, except that the presence of dust layers
can give rise to a more severe classification than would otherwise be the
case (see Table 6.3) as, instead of dispersing, the dust settles on the ground.
In many ways an indoor situation, where air movement is small, can be
advantageous insofar as longevity of dust clouds is concerned. While this
appears to be an advantage it is mitigated by the fact that the layer of
dust so formed can be disturbed and mate a cloud and is, itself, ignition
capable.
Zone 20
A continuous grade source of release will give a Zone 20 from the cloud it
creates, be it indoors or outdoors and only the extent will vary dependent
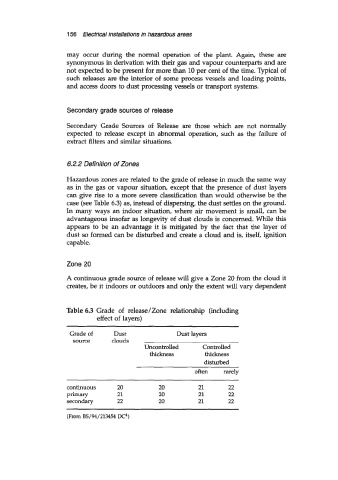
Table 6.3 Grade of release/Zone relationship (including
effect of layers)
Grade of Dust Dust layers
source clouds
Uncontrolled Controlled
thickness thickness
disturbed
often rarely
continuous 20 20 21 22
Primary 21 20 21 22
secondary 22 20 21 22
(From BS/94/213454 LX4)