Page 197 - Electromechanical Devices and Components Illustrated Sourcebook
P. 197
Chapter 9 Connectors 159
Variations on the BNC are the MHV and the SHV connec-
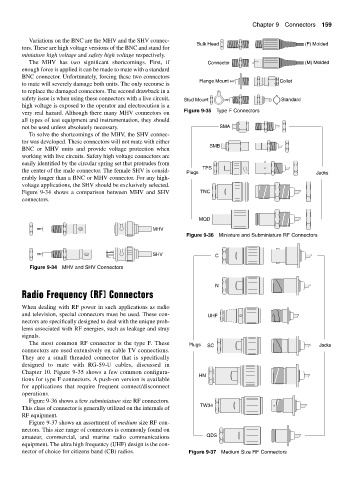
Bulk Head (F) Molded
tors. These are high voltage versions of the BNC and stand for
miniature high voltage and safety high voltage respectively.
The MHV has two significant shortcomings. First, if Connector (M) Molded
enough force is applied it can be made to mate with a standard
BNC connector. Unfortunately, forcing these two connectors
Flange Mount Collet
to mate will severely damage both units. The only recourse is
to replace the damaged connectors. The second drawback in a
safety issue is when using these connectors with a live circuit, Stud Mount Standard
high voltage is exposed to the operator and electrocution is a
very real hazard. Although there many MHV connectors on Figure 9-35 Type F Connectors
all types of test equipment and instrumentation, they should
not be used unless absolutely necessary. SMA
To solve the shortcomings of the MHV, the SHV connec-
tor was developed. These connectors will not mate with either
SMB
BNC or MHV units and provide voltage protection when
working with live circuits. Safety high voltage connectors are
easily identified by the circular spring set that protrudes from
TPS
the center of the male connector. The female SHV is consid- Plugs Jacks
erably longer than a BNC or MHV connector. For any high-
voltage applications, the SHV should be exclusively selected.
Figure 9-34 shows a comparison between MHV and SHV TNC
connectors.
MQD
MHV
Figure 9-36 Miniature and Subminiature RF Connectors
SHV C
Figure 9-34 MHV and SHV Connectors
N
Radio Frequency (RF) Connectors
When dealing with RF power in such applications as radio
and television, special connectors must be used. These con- UHF
nectors are specifically designed to deal with the unique prob-
lems associated with RF energies, such as leakage and stray
signals.
The most common RF connector is the type F. These Plugs SC Jacks
connectors are used extensively on cable TV connections.
They are a small threaded connector that is specifically
designed to mate with RG-59-U cables, discussed in
Chapter 10. Figure 9-35 shows a few common configura-
HN
tions for type F connectors. A push-on version is available
for applications that require frequent connect/disconnect
operations.
Figure 9-36 shows a few subminiature size RF connectors.
TW34
This class of connector is generally utilized on the internals of
RF equipment.
Figure 9-37 shows an assortment of medium size RF con-
nectors. This size range of connectors is commonly found on
amateur, commercial, and marine radio communications QDS
equipment. The ultra high frequency (UHF) design is the con-
nector of choice for citizens band (CB) radios. Figure 9-37 Medium Size RF Connectors