Page 130 -
P. 130
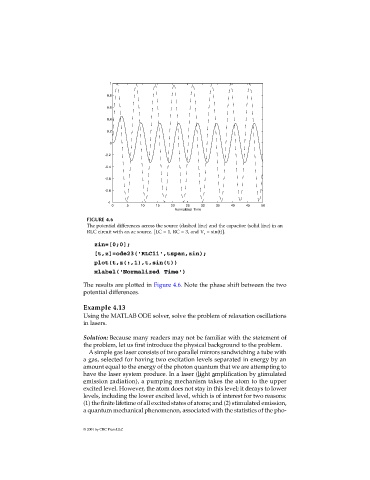
FIGURE 4.6
The potential differences across the source (dashed line) and the capacitor (solid line) in an
RLC circuit with an ac source. [LC = 1, RC = 3, and V s = sin(t)].
zin=[0;0];
[t,z]=ode23('RLC11',tspan,zin);
plot(t,z(:,1),t,sin(t))
xlabel('Normalized Time')
The results are plotted in Figure 4.6. Note the phase shift between the two
potential differences.
Example 4.13
Using the MATLAB ODE solver, solve the problem of relaxation oscillations
in lasers.
Solution: Because many readers may not be familiar with the statement of
the problem, let us first introduce the physical background to the problem.
A simple gas laser consists of two parallel mirrors sandwiching a tube with
a gas, selected for having two excitation levels separated in energy by an
amount equal to the energy of the photon quantum that we are attempting to
have the laser system produce. In a laser (light amplification by stimulated
emission radiation), a pumping mechanism takes the atom to the upper
excited level. However, the atom does not stay in this level; it decays to lower
levels, including the lower excited level, which is of interest for two reasons:
(1) the finite lifetime of all excited states of atoms; and (2) stimulated emission,
a quantum mechanical phenomenon, associated with the statistics of the pho-
© 2001 by CRC Press LLC