Page 67 - Bruno Linder Elementary Physical Chemistry
P. 67
August 18, 2010 11:36 9in x 6in b985-ch06 Elementary Physical Chemistry
52 Elementary Physical Chemistry
8.77 × 10 −2 mol/kg. The elevation of the boiling point is ∆T b = T b −
373.25 K = m b K b .Thus,
T b = 373.25 K + 8.77 × 10 −2 mol/kg × 0.51 K kgmol −1
= (373.25 + 0.0447)K = 373.29 K.
6.2.5. Osmotic Pressure
It was observed a long time ago that when a cylinder containing wine was
covered with animal membranes and placed in a bucket of water, the bladder
swelled. The increased pressure in the tube is called osmotic pressure.
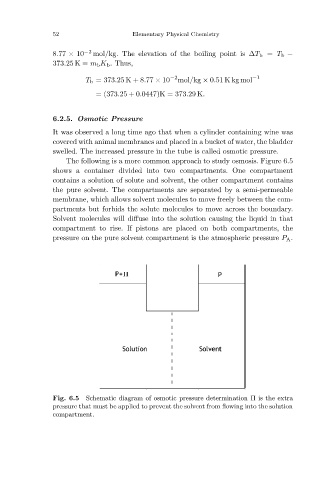
The following is a more common approach to study osmosis. Figure 6.5
shows a container divided into two compartments. One compartment
contains a solution of solute and solvent, the other compartment contains
the pure solvent. The compartments are separated by a semi-permeable
membrane, which allows solvent molecules to move freely between the com-
partments but forbids the solute molecules to move across the boundary.
Solvent molecules will diffuse into the solution causing the liquid in that
compartment to rise. If pistons are placed on both compartments, the
pressure on the pure solvent compartment is the atmospheric pressure P A .
Schematic diagram of osmotic pressure determination Π is the extra
Fig. 6.5
pressure that must be applied to prevent the solvent from flowing into the solution
compartment.