Page 129 - Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering 3rd Edition
P. 129
Sec. 3.3 Stoichiometric Table 101
0.251 I I I I I I 1 1
Conversion, X
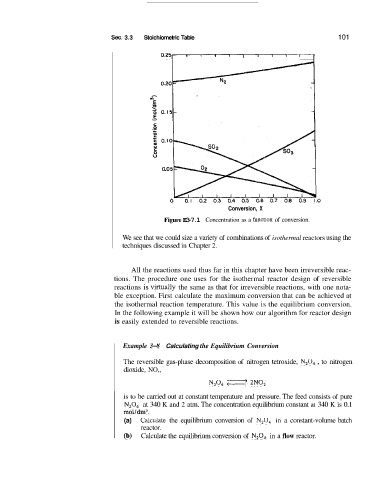
Figure E3-7.1 Concentration as a functi,on of conversion.
We see that we could size a variety of combinations of isothermal reactors using the
techniques discussed in Chapter 2.
All the reactions used thus far in this chapter have been irreversible reac-
tions. The procedure one uses for the isothermal reactor design of reversible
reactions is virlually the same as that for irreversible reactions, with one nota-
ble exception. First calculate the maximum conversion that can be achieved at
the isothermal reaction temperature. This value is the equilibrium conversion.
In the following example it will be shown how our algorithm for reactor design
is easily extended to reversible reactions.
Example 3-8 Calculating the Equilibrium Conversion
The reversible gas-phase decomposition of nitrogen tetroxide, N204 , to nitrogen
dioxide, NO,,
N204 e
2N02
is to be carried out at constant temperature and pressure. The feed consists of pure
N204 at 340 K and 2 atm. The concentration equilibrium constant at 340 K is 0.1
mol/dm3.
(a) Calcula1.e the equilibrium conversion of N,04 in a constant-volume batch
reactor.
(b) Calculate the equilibrium conversion of N204 in a flow reactor.