Page 138 - Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering 3rd Edition
P. 138
110 Rate Laws and Stoichiometry Chap. 3
We must use the column in the stoichiometric table labeled “after condensation” in
conjunction with Equation (E3-10.11) to determine CA and C,.
c -EL 1.5 FAO(1 -X) = 1.5 CAo(1-y ) -
1-x
(E3-10.12)
A - U U0(1.5-x)/(1 -yo,e) D2e 1.5 -X
FB 1.5 FA0(2 -2X)
c -_= = ‘AO(’ -YD,e) -’ (E3-10.13)
- u ~~(1.5 -X)/(l -yD,=)
The rate law for X > X, is
I I
(E3- 10.14)
Before condensation, for X < X,, the gas-phase molar flow rate of D is FD = FAOX.
After condensation begins (Le., X > X,), the mdar flow rate of D in the gas phase is
YO e
FD(g) =YD,~FT= 2FAo(1.5-X) = 0.375 FAo(1.5FX) (E3-10.
- YD,e
The liquid molar flow rate of D is
FD(~) FA&-FD(~) = F~o(1.375x-0.563)
=
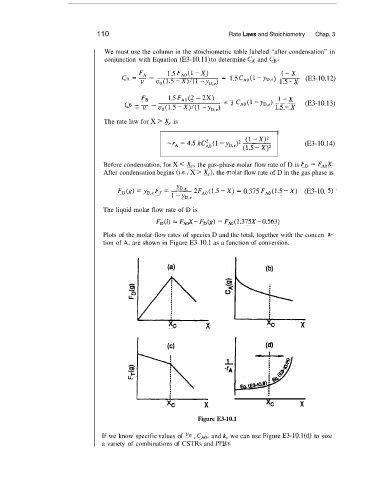
Plots of the molar flow rates of species D and the total, together with the concen
tion of A, are shown in Figure E3-10.1 as a function of conversion.
XC X x, X
x, X x, X
Figure E3-10.1
If we know specific values of uo , CAo, and k, we can use Figure E3-10.l(d) to size
a variety of combinations of CSTRs and PFRs.