Page 136 - Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering 3rd Edition
P. 136
108 Rate Laws and Stoichiometry Chap. 3
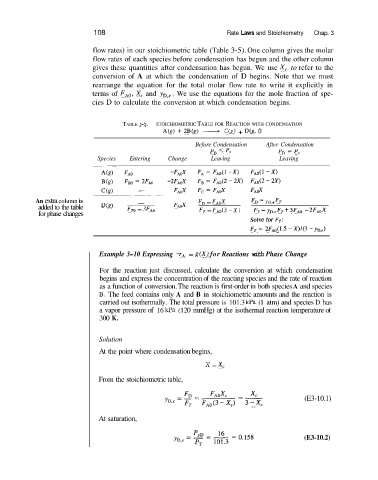
flow rates) in our stoichiometric table (Table 3-5). One column gives the molar
flow rates of each species before condensation has begun and the other column
gives these quantities after condensation has begun. We use X, to refer to the
conversion of A at which the condensation of D begins. Note that we must
rearrange the equation for the total molar flow rate to write it explicitly in
terms of FAo, X, and Y~,~. We use the equations for the mole fraction of spe-
cies D to calculate the conversion at which condensation begins.
TABLE 3-5. STOICHIOMETRIC TABLE FOR REACTION WITH CONDENSATION
A(g) + 2b(g) --+ C(g) + D(g, 0
Before Condensation After Condensation
< p~ PO = P”
Species Entering Change Leaving Leaving
An extra column is - FD = FAOX FD = YO, e FT
added to the table (” F, = 3 FAo
for phase changes FT = FAO(3 - X) F, = yD,e FT f 3FA, - 2FA0X
Example 3-10 Expressing -rA = g(X) for Reactions with Phase Change
For the reaction just discussed, calculate the conversion at which condensation
begins and express the concentration of the reacting species and the rate of reaction
as a function of conversion. The reaction is first-order in both species A and species
€3. The feed contains only A and B in stoichiometric amounts and the reaction is
carried out isothermally. The total pressure is 101.3 kPa (1 atm) and species D has
a vapor pressure of 16 kPa (1 20 mmHg) at the isothermal reaction temperature of
300 K.
Solution
At the point where condensation begins,
x = xc
From the stoichiometric table,
(E3-10.1)
At saturation,
(E3-10.2)