Page 147 - Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering 3rd Edition
P. 147
Chap. 3 Questions and Problems 119
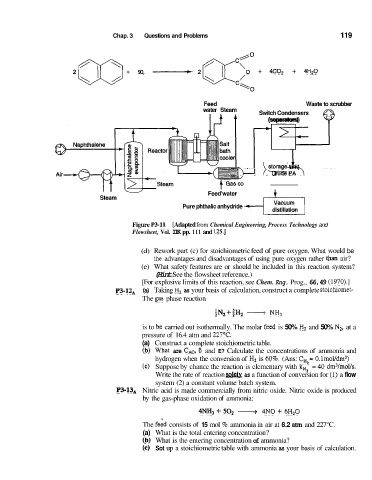
2 fJ-J +. 90, -- 2 0 + 4130, + 4H20
oler rF
Feed Waste to scrubber
water Steam Switch Condensers a
(separators)
1- btyge tank)
(r CrudePA
Feed'water
Steam
Pure phthalic anhydride
distillation
Figure P3-11 [Adapted from Chemical Engineering, Process Technology and
Flowsheet, Vol. IIK pp. 11 1 and 125.1
(d) Rework part (c) for stoichiometric feed of pure oxygen. What would be
the advantages and disadvantages of using pure oxygen rather than air?
(e) What safety features are or should be included in this reaction system?
(Hint: See the flowsheet reference.)
[For explosive limits of this reaction, see Chem. Eng. Prog., 66, 49 (1970).]
P3-12!* (a) Taking H2 as your basis of calculation, construct a complete stoichiomet-
The gas phase reaction
iN2fiH2 --+ NH3
is to be carried out isothermally. The molar fwd is 50% H2 and 50% IU,, at a
pressure of 16.4 atm and 227OC.
(a) Construct a complete stoichiometric table.
0) W'hat are CAo, 6 and E? Calculate the concentrations of ammonia and
hydrogen when the conversion of H2 is 60%. (Ans: CHz= O.imoYh3)
(e) Suppose by chance the reaction is elementary with kN2 = 40 dm3/moYs.
a
Write the rate of reaction g&ly as a function of conversion for (l)~ flow
system (2) a constant volume batch system.
P3-13& Nitric acid is made commercially from nitric oxide. Nitric oxide is produced
by the gas-phase oxidation of ammonia:
4NH3+50, + 4N0+6H20
The feth consists of 15 mol % ammonia in air at 8.2 am and 227°C.
(a) What is the total entering concentration?
(b) What is the entering concentration of ammonia?
(e) Sot up a stoichiometric table with ammonia as your basis of calculation.