Page 187 - Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering 3rd Edition
P. 187
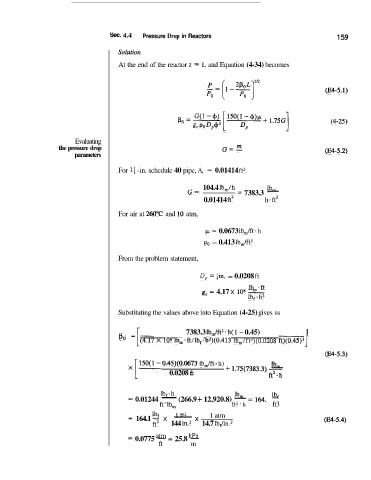
Sec. 4.4 Pressure Drop in Reactors 1 59
Soltition
At the end of the reactor z = L and Equation (4-34) becomes
(E4-5.1)
(4-25)
Evaluating
the pressure drop (E4-5.2)
parameters
For 1; -in. schedule 40 pipe, A, = 0.01414 ft2:
104.4 lb,/h = 7383.3 -
1bm
G=
0.01414 ft2 h * ft2
For air at 260°C and 10 atm,
p = 0.0673 lb,/ft. h
po = 0.413 lb,/ft3
From the problem statement,
D, = !in. = 0.0208 ft
lb aft
g, = 4.17 X lo8
Ib, - h2
Substituting the values above into Equation (4-25) gives us
-
7383.3 lb,/ft2. h( 1 - 0.45) 1
= l(4.17 X lo8 Ib,*ft/lb,. h2)(04413 lb,/ft3)(0.0208 ft)(O.45)31
(E4-5.3)
0.45)(0.0673 lb,/ft - h) + 1.75(7383.3) -
0.0208 ft
1bf.h 1brn 'bf -
= 0.01244 - (266.9 + 12,920.8) - 164.
=
ft Ib, ft2 h ft3
= 164.1 - X -
lb,
1 ft2
1 atm
x
ft3 144 in.2 14.7 lbf/in.2 (E4-5.4)
= 0.0775 - 25.8 -
kPa
atm
=
ft m