Page 195 - Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering 3rd Edition
P. 195
Sec. 4.4 Pressure Drop in Reactors 167
It is also interesting to learn what happens to the volumetric flow rate along the
length of the reactor. Recalling Equation (3-44),
Po T - u,(l +EX)(T/T,)
u = U0(1+EX) - - - - (3-44)
p To P/Po
We let f be the ratio of the volumetric flow rate, u, to the entering volumetric flow
rate, uo, at any point down the reactor. For isothermal operation Equation (3-44)
Volumetric flow becomes
rate increases
with increasing
pressure drop
(E4-7.5)
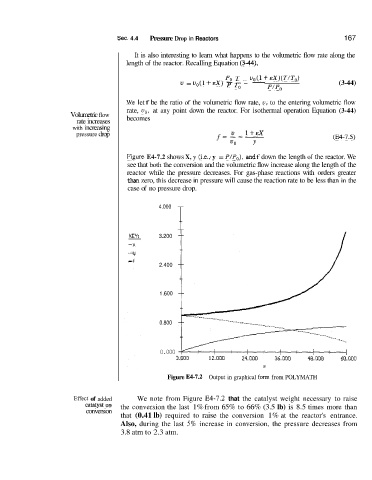
Rgure E4-7.2 shows X, y (i.e., y = P/Po), and f down the length of the reactor. We
see that both the conversion and the volumetric flow increase along the length of the
reactor while the pressure decreases. For gas-phase reactions with orders greater
than zero, this decrease in pressure will cause the reaction rate to be less than in the
case of no pressure drop.
i
4.000
3.200
2.400
1.600
0.800
0.000
W
Figure E4-7.2 Output in graphical form from POLYMATH
Effect of added We note from Figure W-7.2 that the catalyst weight necessary to raise
on the conversion the last 1% from 65% to 66% (3.5 lb) is 8.5 times more than
conversion
that (0.41 lb) required to raise the conversion 1% at the reactor's entrance.
Also, during the last 5% increase in conversion, the pressure decreases from
3.8 atm to 2.3 atm.